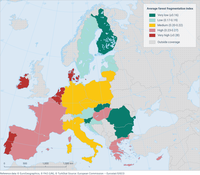
This figure shows the average forest fragmentation index for each Member State in 2018. Fragmentation is calculated as the share of forested land not covered by forest or small woody features in a local neighborhood of 10 hectares surrounding the focal 100 m² forest grid cell.

Biodiversity is vital for healthy ecosystems and the foundation of our well-being and economy. However, it is under severe threat. At the root of the problem, lies our current unsustainable production and consumption systems. The circular economy is key to transforming these systems. This briefing explores how circular economy can reduce the impacts of production and consumption on biodiversity

Biodiversity is vital for healthy ecosystems and the foundation of our well-being and economy. However, it is under severe threat. At the root of the problem, lies our current unsustainable production and consumption systems. The circular economy is key to transforming these systems. This briefing explores how circular economy can reduce the impacts of production and consumption on biodiversity

Nature, along with its inherent biodiversity, is key to functioning societies and economies. It provides the food we eat, filters the water we drink, cleans the air we breathe, and is important for our mental and physical health. Yet in the EU, many habitats and species are in a poor or bad state, and only a very small fraction of these has shown any improvement over recent years. The restoration of Europe’s habitats and species is important not only for the inherent value of nature itself: it is also key for improved human health and well-being, and reduced climate change impacts.

Nature, along with its inherent biodiversity, is key to functioning societies and economies. It provides the food we eat, filters the water we drink, cleans the air we breathe, and is important for our mental and physical health. Yet in the EU, many habitats and species are in a poor or bad state, and only a very small fraction of these has shown any improvement over recent years. The restoration of Europe’s habitats and species is important not only for the inherent value of nature itself: it is also key for improved human health and well-being, and reduced climate change impacts.
Country data from European database on disturbances

Deforestation in the EU-27 as collected by countries for the reporting on forest resources to the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and Forest Europe processes
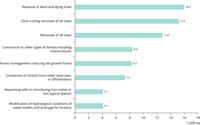
The eight most relevant pressures on forests from forestry activities.
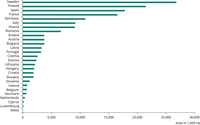
Forest area in the EU-27 as collected by countries for the reporting on forest resources to the UNECE, FAO and Forest Europe processes

The figure shows marine protected areas coverage in the EU in 2012-2021.

The combo charts show the number of new introductions of non-indigenous species (NIS) (dots with trendline, primary axis) and the cumulative number of NIS by main species group (stacked columns, secondary axis) reported in Europe’s marine subregions, per 6-year interval between 1970 and 2017.

The figure shows the number of new non-indigenous species (NIS) reported by marine region. The line-bar chart shows the total number of new introductions of NIS (grey bars) and by main species group (lines) reported in Europe’s seas combined and by marine region, per 6-year interval between 1970 and 2017. The stacked column charts show the cumulative number of new NIS introductions by main species group, in Europe’s seas combined and by marine region, per 6-year interval between 1970 and 2020.

The pie chart shows the share of the different pathways of introduction of new non-indigenous species (NIS) to Europe's seas over the years 1970 to 2020. The category 'Other' includes several modes of introduction, namely 'Transport-stowaway: other', 'release in nature', 'escape from confinement', 'corridor' and 'unknown'. The stacked column chart shows the trend in the number of new NIS by pathway of introduction between 1970 and 2017, on a 6-year cycle. While introductions by Transport-Stowaway (ballast water, hull fouling and others) remain the prevalent mode, 'unaided' and 'escape from confinement' have grown in importance in the latest assessment cycles.
Document Actions
Share with others