All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesJeans, raincoats, curtains, bedlinen, shoes, sportswear... The list is endless. We all need and use textile products. Textile consumption in Europe causes on average the fourth highest pressure on the environment and climate, following consumption of food, housing and mobility.
In the last few decades, the textile industry has evolved towards a “fast fashion” approach: inexpensive clothes, made of cheap materials, to be worn only for one season or less and then discarded. The production and consumption of textiles cause significant pressures on the environment and climate change. These can range from the land and water used to produce the fibres and the energy and chemical dyes used in its manufacturing and production, to its retailing and disposal.
Our assessments show that, compared with other consumption categories, textiles consumption in the EU caused in 2020 the third highest pressures on water and land use, and the fifth highest use of raw materials and greenhouse gas emissions.
At the same time, worldwide, the textiles sector is the third largest employer, after food and housing, with almost 13 million full-time equivalent workers employed worldwide in the supply chain to produce the amount of clothing, textiles and footwear consumed only in the EU-27 in 2020. Most production takes place in Asia, where low production costs often come at the expense of workers’ health and safety.
Circular business models and design can reduce the negative impacts of textile production and consumption by retaining the value of textiles, extending their life cycles and increasing the usage of recycled materials. This requires technical, social and business innovation, supported by policy, education and changes in consumer behaviour.

Textiles consumption is rising, highlighting the need to circularity efforts
EU citizens consumed on average 19 kg of clothing, footwear and household textiles in 2022 — up from 17 kg in 2019 — placing textiles among the top five household consumption categories for environmental and climate pressures in the EU.
This EEA briefing presents new data underpinned by the Circularity Metrics Lab (CML), highlighting that fast fashion and low collection rates continue to hinder reuse and recycling, while a systemic shift to durable, high-quality and circular textiles is needed.
Safe and sustainable alternatives could reduce use of PFAS in textiles
Textiles are one of the biggest sources of PFAS pollution in Europe. Polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS), a group of highly persistent chemicals, are widely used in many textile-based products including clothing, carpets and other household goods for waterproofing, oil, dirt and heat protection, and increased durability.
Reducing the use of PFAS —known as forever chemicals— in clothing, furniture and other textile products, is important to increase recyclability and the transition to a more circular economy according to a European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing.

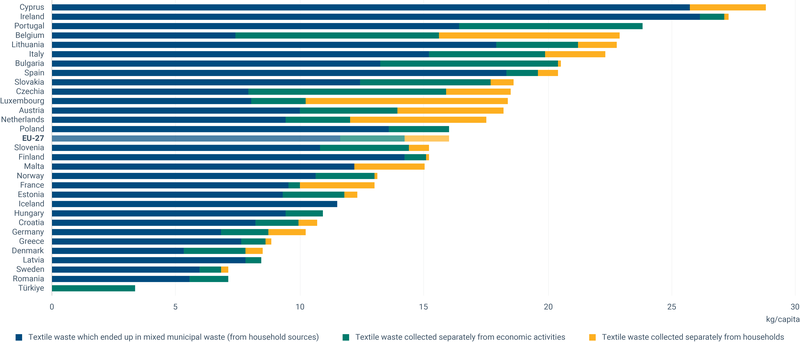
Most textile waste goes unsorted in Europe
Starting with 2025, EU Member States must put separate collection systems in place for textiles. Our EEA briefing shows that most textile waste in Europe currently ends up in mixed waste and that sorting and recycling capacity need to be urgently scaled up to ensure better and more circular use of used textiles.
According to the EEA estimate, around 16 kg of textile waste per person was generated in the EU in 2020. Only about one quarter of this amount (4.4 kg) was collected separately for reuse and recycling, but the rest ended up in mixed household waste. Of all textile waste, 82% came from consumers and the rest was waste from manufacturing or textiles that were never sold.
Europe's used textile exports: what and where?
Europe faces major challenges in the management of used textiles, which are to be collected separately in the EU by 2025. As reuse and recycling capacities in Europe are limited, a large share of discarded and donated clothing and other textile products are exported.
- The amount of used textiles exported from the EU has tripled over the past two decades from slightly over 550,000 tonnes in 2000 to almost 1.7 million tonnes in 2019.
- The amount of used textiles exported in 2019 was on average 3.8 kilogrammes per person, or 25% of the approximately 15 kg of textiles consumed each year in the EU.
- In 2019, 46% of used textiles exported from the EU ended up in Africa. The textiles primarily go to local reuse as there is a demand for cheap, used clothes from Europe. What is not fit for reuse mostly ends up in open landfills and informal waste streams.
- In 2019, 41% of used textiles exported from the EU ended up in Asia. Most of these textiles are directed to dedicated economic zones where they are sorted and processed.


Many returned and unsold textiles end up destroyed in Europe
Textile consumption in Europe causes significant pressures on the environment and climate. Part of these pressures comes from returned and unsold textiles that are destroyed and never used for their intended purpose.
Around 4-9% of all textile products put on the European market are destroyed without ever being used for their intended purpose. According to the EEA briefing, processing and destructing returned or unsold textiles can be estimated to be responsible for up to 5,6 million tonnes of CO2-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions, a figure that is slightly lower that Sweden’s net emissions in 2021.

Textiles as a source of microplastic pollution
Over 14 million tonnes of microplastics have accumulated on the world’s ocean floor according to research estimates. The amounts are increasing every year — causing harm to ecosystems, animals and people. About 8% of European microplastics released to oceans are from synthetic textiles. Globally, this figure is estimated around 16-35%.
The majority of microplastics from textiles are released the first few times textiles are washed. Fast fashion accounts for particularly high levels of such releases because fast fashion garments account for a high share of first washes, as they are used for only a short time and tend to wear out quickly due to their low quality.
It is possible to reduce or prevent the release of microplastics from textiles, for instance by implementing sustainable design and production processes and caretaking measures that control microplastic emissions during use, and by improving disposal and end-of-life processing.

