All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesClimate change affects us all and is accelerating. Its impacts will become even more severe if the increase in global temperature is not kept below 1.5°C. The EU and its Member States are taking important steps to rapidly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities — mainly from burning fossil fuels, industrial production and agricultural activities are causing our climate to change at a rapid pace. Climate change is already impacting Europeans’ daily lives and will continue for the foreseeable future.
Already, flooding, droughts, heatwaves and other climate-related hazards are becoming more intense and frequent in Europe and abroad. These hazards have significant health and economic costs, while also impacting ecosystems. Without increased ambition and rapid action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the impacts of climate change will continue and intensify.
Dealing with climate change requires two interlinked actions working together:
- Climate change mitigation: reducing the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and enhancing their sinks to slow down climate change.
- Climate change adaptation: actions to adapt to the impacts of climate change, like preventing flooding, preparing for heatwaves and reducing other climate risks.
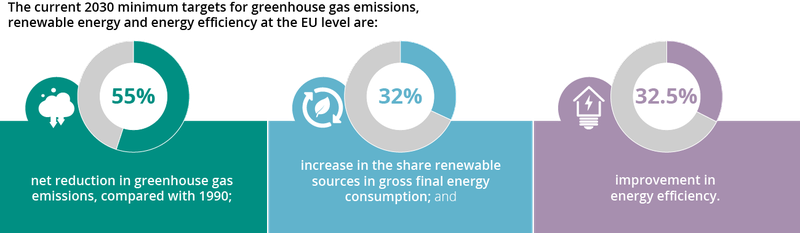
With the European Climate Law, the EU made climate neutrality by 2050 a legally binding goal, set an interim target of a net 55% emission reduction by 2030 and is working on setting the 2040 target. The overarching framework for these is the European Green Deal, a roadmap for the EU to achieve sustainability by 2050.
EU's climate targets at a glance
Source: EEA Signals 2022 — State of play
EU greenhouse gas emissions see significant drop in 2023
Total net greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union dropped by 8% in 2023, marking significant progress towards climate neutrality for the EU. The huge drop was led by a significant decline in coal use and growth of renewable energy sources and supported by reduced energy consumption across Europe, according to estimated figures included in the latest European Environment Agency (EEA) ‘Trends and Projections’ report.
Based on reported existing climate measures alone, Member State projections forecast a reduction in net emissions by 2030 to a level 43% below 1990 levels. However, 22 Member States have submitted additional projections that include planned but not yet launched measures. Together, these would reduce net emissions in the EU by 49% below 1990 levels in 2030, in the target scope of the EU Climate Law.


Europe is not prepared for rapidly growing climate risks
Europe is the fastest warming continent in the world, and climate risks are threatening its energy and food security, ecosystems, infrastructure, water resources, financial stability, and people’s health.
Extreme heat, drought, wildfires, and flooding, as experienced in recent years, will worsen in Europe even under optimistic global warming scenarios and affect living conditions throughout the continent. The EEA has published the first ever European Climate Risk Assessment (EUCRA) to help identify policy priorities for climate change adaptation and for climate-sensitive sectors.
According to our assessment, many of these risks have already reached critical levels and could become catastrophic without urgent and decisive action.
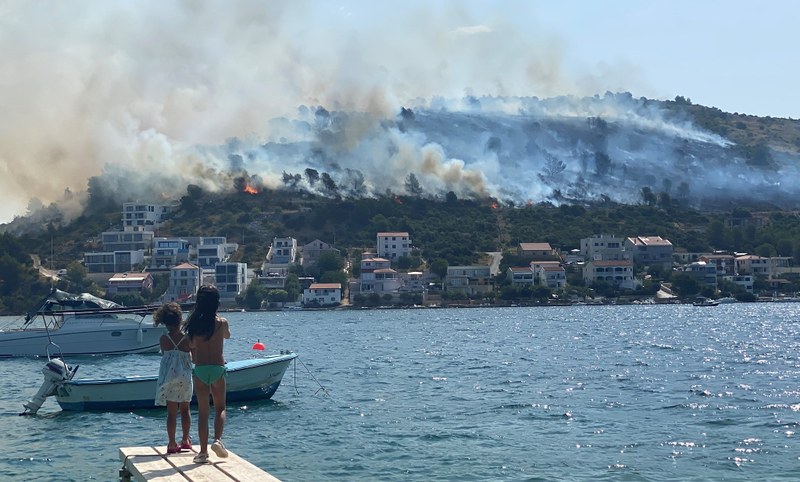
Changing climate and Europe’s summer
Heatwaves, floods, droughts and wildfires have become more common in Europe during summer months, and May 2024 was the 12th consecutive month with record-high temperatures, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S).
In June 2024, the devastating floods in Germany caused several fatalities and significant economic damages.
The season of possible droughts, forest fires, extreme rain and flooding is ahead of us. The European Environment Agency offers key resources to better understand extreme summer weather in Europe.

Dive deeper

What causes climate change?
By burning fossil fuels, producing goods, cutting down forests, and farming livestock, Earth’s average temperatures are heating up. These activities release massive amounts of greenhouse gases into our atmosphere, which increases the greenhouse effect and causes global warming. There are four main types of greenhouse gases created by human activity:
- Carbon dioxide, stemming mainly from transport, coal, oil, deforestation and natural gas burned to generate heat and electricity;
- Methane primarily from livestock waste management and fugitives from coal, oil and gas operations;
- Nitrous oxide from fertiliser use;
- Fluorinated gases from manufacturing and industry.
Is Europe on track towards climate resilience? Status in 2023
Climate risk assessments that take account of threats like heatwaves, droughts, floods and wildfires are increasingly being used to inform and improve national adaptation policies according to the latest European Environment Agency (EEA) assessment of national adaptation actions.
Heatwaves, droughts, floods and increasing wildfires were the top extreme weather events reported by national authorities. Many countries also reported that they expected an increase of frequency and intensity of these events.






