
Natura 2000 data refers to information reported by Member States by the end of 2022. Europe's seas are defined by the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) marine regions (in bold below) and subregions.

The figure shows changes in population abundance of 15 grassland butterfly species at EU level, using 1991 as reference year. The grassland butterfly index is presented as a smoothed time series and is calculated with 95% confidence limits.

The map shows the share of woody landscape features in agricultural areas on NUTS3 regions.

The charts show:
Top figures: the temporal development in the number of species of each biogeographical affinity group (Atlantic, Boreal, Lusitania and Unknown) by marine region (Greater North Sea, Baltic Sea, Celtic Seas and Bay of Biscay and the Iberian Coast).
Bottom figures: the temporal development of the ratio between Lusitanian and Boreal species and sea surface temperature by marine region to investigate correlations.

The maps show the temporal development of the ratio between the number of warm-favouring (Lusitanian) fish species and the number of cool-favouring (Boreal) fish species by The International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) statistical area in 8-year intervals from 1982 to 2022.
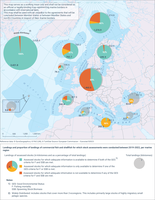
The figure shows the proportion of commercial European fish landings assessed per regional sea distinguishing between assessed and non-assessed stocks. For the assessed stocks a distinction is made between (i) landings of stocks for which information is available to determine Good Environmental Status (GES) for Fishing mortality (F) and/or Spawning Stock Biomass (SSB) and (ii) landings for stocks for which information is not available to determine GES for F and/or SSB.
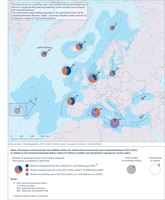
This figure shows the state of the assessed commercially exploited fish and shellfish stocks per European marine region, for which assessments were conducted in 2019-2022. Stocks for which adequate information is available to determine Good Environmental Status (GES) for fishing mortality (F) and/or reproductive capacity (spawning stock biomass (SSB)) are included (i.e. Z, total number of stocks; Y, total number of assessed stocks; and X, number of stocks for which adequate information is available to determine GES on the basis of these two criteria). A distinction is made between stocks: (1) in good status based on both fishing mortality and reproductive capacity; (2) in good status based on only one of the criteria - fishing mortality or reproductive capacity (either because one of the two criteria is not in good status or because there is only one available criteria, and it is in good status); and (3) not in good status based on both fishing mortality and reproductive capacity (may include cases where only one criteria is available and it is not in good status).

This figure shows trends in the status of assessed commercially exploited fish and shellfish stocks between 1947 and 2021, expressed in two metrics-fishing mortality (F) and reproductive capacity (i.e. spawning stock biomass (SSB))-relative to their policy thresholds for the Marine Strategy Framework Directive's 'good environmental status' (GES) (i.e. FMSY and MSY Btrigger, respectively).
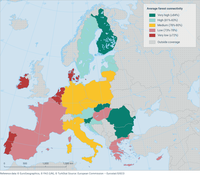
This figure shows the average forest connectivity for each EU member state in 2018. Forest connectivity is calculated as the share of land covered by forest or small woody features in a local neighbourhood of 10 hectares surrounding the focal forest grid cell.

The map shows the ecosystem area at risk of eutrophication for 2021
Document Actions
Share with others