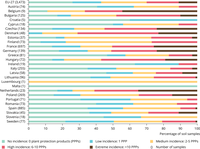
The figure shows the percentage of soil samples for each country with a specified number of detections of pesticides, based on analysis of 118 different pesticides in the samples.


This map shows a mixture toxicity metric called multi-substance Potentially Affected Fraction of species (msPAF). For individual substances, the Potentially Affected Fraction of species (PAF) is derived from the results from laboratory toxicity tests, as the fraction of the tested species that would show effects if a laboratory test would be performed with a given concentration of the chemical. To this end, the results from laboratory tests have been converted beforehand into a species sensitivity distribution (SSD). The individual PAFs are then combined into an msPAF using the dose-addition principle. For this map, toxicity tests have been used that seek to quantify the no-observed-effect concentration (NOEC). The use of this endpoint links the result to the regulatory concept of “sufficient protection” of aquatic ecosystems. The above has been applied to the simulated concentrations of 1,785 chemicals on 365 consecutive days, and the 95 percentile of the results per site have been mapped.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment presents available knowledge and trends on soil pollution and associated impacts on ecosystems, and assesses progress towards achieving relevant zero pollution targets and policy objectives.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment examines available knowledge and trends in pollution and associated impacts on ecosystems. In addition to this summary assessment page there are sub-sections providing more detailed analysis on freshwater pollution, marine pollution, air pollution and soil pollution impacts on ecosystems. A collection of ‘Signals’ is also provided which highlight emerging issues and other available knowledge on pollution of ecosystems.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment presents a series of short case studies that highlight additional sources of information on the impacts of pollution on freshwater ecosystems.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment presents available knowledge and trends on freshwater pollution and associated impacts on ecosystems, and assesses progress towards achieving relevant zero pollution targets and policy objectives.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment presents a series of short case studies that highlight additional sources of information on the impacts of pollution on ecosystems.

This section of the zero pollution monitoring assessment presents a series of short case studies that highlight additional sources of information on the impacts of air pollution on ecosystems.

Biodiversity is strongly declining in Europe and across the world. To reverse this, we need to use all available tools to strengthen actions taken by governments, businesses and consumers. Public policy tools (such as establishing nature reserves, regulating hunting and fishing, and providing support for biodiversity-friendly farming) are widely used to tackle biodiversity loss. However, the actions of consumers and businesses are also very important. This briefing focuses on key areas for further development to build the knowledge that is needed to finance biodiversity.

Biodiversity is strongly declining in Europe and across the world. To reverse this, we need to use all available tools to strengthen actions taken by governments, businesses and consumers. Public policy tools (such as establishing nature reserves, regulating hunting and fishing, and providing support for biodiversity-friendly farming) are widely used to tackle biodiversity loss. However, the actions of consumers and businesses are also very important. This briefing focuses on key areas for further development to build the knowledge that is needed to finance biodiversity.
Natura 2000 is the key instrument to protect biodiversity in the European Union. It is an ecological network of protected areas, set up to ensure the survival of Europe's most valuable species and habitats. Natura 2000 is based on the 1979 Birds Directive and the 1992 Habitats Directive. This version covers the reporting in 2021, revision 1. Two member states, Germany and Ireland, were rolled back to their previous submissions in the European dataset.

Natura 2000 data refers to information reported by Member States by the end of 2021. Europe's seas are defined by the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) marine regions (in bold below) and subregions.

The dataset “Extended wetland ecosystem” is a derived product of the Corine Land Cover (CLS) layer for the year 2018 which has then been reclassified into 20 wetland classes on the basis of ancillary spatial layers (“Water and Wetness 2018” and “Riparian Zone Layer” Copernicus products, the “Ecosystem types of Europe” v3.1 and “The Global Spatial Water Explorer” datasets).
Besides the traditional types of inland and coastal wetlands (i.e. marshes, rivers, lakes, lagoons, estuaries), the layer also covers the forest, grassland and agricultural ecosystems which are seasonally or permanently flooded (i.e. riparian forests, wet grasslands, rice fields) and are therefore considered as wetlands according to the Ramsar Convention definition and typology. This wetland reclassification and mapping considers their hydro-ecological characteristics and provides information about the real spatial extent and distribution of varied wetland habitats.

All Member States are requested by EU Regulation 1143/2014 to report every 6 years on the Invasive Alien Species (IAS) of Union, of regional and of Member State concern and to provide information on cross-cutting issues of the implementation of the Regulation.
Document Actions
Share with others