
Digital technologies like robotics, cloud computing and artificial intelligence will help improve the sustainability of Europe’s waste management systems. According to a European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing released today, increased use of these technologies can help deliver more effective waste management across Europe, improving logistics, recycling rates and enable better purchasing and sorting decisions by consumers.

COUNCIL DECISION (EU) 2017/1541 of 17 July 2017 on the conclusion, on behalf of the European Union, of the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol on substances that deplete the ozone layer

Our joint Strategy indicates our direction of travel. It introduces a new way of working together and creating knowledge — more agile, more responsive, more pro-active, more actionable — befitting the challenges we will face and the knowledge we will need in the decade to come.

Air pollution, noise pollution and the impacts of climate change are key risks to the everyday health and well-being of Europeans. We talked with Catherine Ganzleben, head of group, air pollution, environment and health, Alberto González, EEA air quality expert, and Eulalia Peris, EEA noise pollution expert to find out more on what the EEA is doing to improve knowledge in this important field of work.

Greenhouse gas emissions from stationary installations covered by the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (ETS) dropped by 9.1% in 2019 from 2018 levels, the largest drop in a decade, according to the latest European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing on trends and projections in the EU ETS released today.

Demand for and use of climate-warming fluorinated gases continues to drop across the European Union, according to the latest annual update of EU progress in phasing down the use of F-gases, published today by the European Environment Agency (EEA). Industry is substituting these F-gases with more climate-friendly products.

Thanks to steady improvements in emission reductions and renewables uptake, the European Union is likely to achieve two of its three 2020 climate and energy targets, namely reducing greenhouse gas emissions and boosting renewable energy, according to the European Environment Agency's (EEA) Trends and Projections report published today. Achieving the third target — reducing energy consumption — still looks unclear.

A vast majority of the European Environment Agency’s (EEA) 39 member and cooperating countries are putting in action United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including those focused on climate action, water and sanitation, and affordable and clean energy, according to a pan-European assessment, published today, of how the SDGs are being implemented.

Directive (EU) 2018/410 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 March 2018 amending Directive 2003/87/EC to enhance cost-effective emission reductions and low-carbon investments, and Decision (EU) 2015/1814

COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT IMPACT ASSESSMENT
Accompanying the document: COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS Stepping up Europe’s 2030 climate ambition - Investing in a climate-neutral future for the benefit of our people

Directive (EU) 2018/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources

Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions (COM(2019) 640 final).

Achieving the 2020 target to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from transport fuels remains problematic for most European Union Member States according to the latest reported data up to 2018 released by the European Environment Agency (EEA) today.

The COVID-19 pandemic and resulting restrictions imposed to fight the spread of the disease have provided some short-term positive impacts on Europe’s environment, according to a European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing published today. These include temporary improvements in air quality, lower greenhouse gas emissions and lower levels of noise pollution. However, the assessment also stresses that there have been negative consequences such as increased use of single-use plastics, and that ways out of the pandemic should focus on reshaping our unsustainable production and consumption systems to achieve long-term environmental benefits.
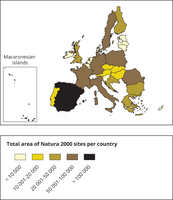
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. The bottom left box refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). It only includes terrestrial Natura 2000 sites for EU-28 (SPAs, SACs, SCIs and proposed SCIs).
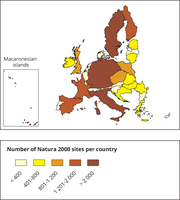
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. The box on the bottom left refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary Islands). It only includes terrestrial Natura 2000 sites for EU-28 (SPAs, SACs, SCIs and proposed SCIs).
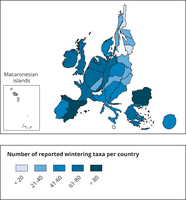
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. Here, the size of the country shows the number of reported species in relation to the country size. The map do not show all species appearing in a country. Thus, the map shows the reporting result rather than the species diversity of a country. The box on the bottom left refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary islands). Romania has not reported and is therefore not included in the map.
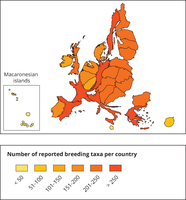
This map is a cartogram that distorts the geometry of regions to convey specific information by resizing. Here, the size of the country shows the number of reported species in relation to the country size. The map do not show all species appearing in a country. Thus, the map shows the reporting result rather than the species diversity of a country. The box on the bottom left refers to the Macaronesian islands (Azores, Madeira and Canary islands). Romania has not reported and is therefore not included in the map.

We know that plastic pollution and plastic waste are a big environmental problem. In recent years, new plastic products have been introduced on the market, claiming to be better for the environment. A recently published European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing assesses their environmental credentials. To find out more, we sat down with Almut Reichel, a sustainable resource use and waste expert at the EEA.

The European Environment Agency together with the network of the heads of Environmental Protection Agencies (EPA Network) today launch the first in a series of online high-level panel debates focusing on the impacts of COVID-19 and the challenges the pandemic poses in meeting long-term climate and environment goals.
Document Actions
Share with others