
Reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are crucial to tackling the impacts of climate change, especially methane gas emissions which are seen as a priority area for action by the EU. The EEA recently published a briefing on methane emissions in the EU which includes a new data visualisation tool. We sat down with Ricardo Fernandez, EEA climate change mitigation expert and coordinator of the EU’s GHG inventory to the UNFCCC, to explain the briefing and why reducing methane emissions is so crucial to wider mitigation efforts.

The zero pollution action plan is a cornerstone of the EU’s ambitions to improve the well-being and health of citizens and future generations under the European Green Deal. It sets out the vision that by 2050, the EU should have reduced pollution to the extent that it no longer harms human health and natural ecosystems. This is translated into key 2030 targets to speed up reducing pollution at source. The European Environment Agency has produced this zero pollution monitoring assessment to assess progress towards these targets and to support the Commission in the delivery of the long-term vision of a non-toxic environment.

The Russian military aggression in Ukraine changed the lives of Ukrainians from one day to the next. The impacts of this unjustified war are felt not only in Ukraine but also well beyond the borders of Ukraine and will continue to impact us all for years and even for generations to come.

Long-term projection of environmental tax revenues in the UK

Overview of changes in environmental tax revenues as a share of total tax revenues in EU-27, EU Member States and Norway between 2002 and 2019

2021 was marked by Covid-19 and climate change impacts. Faced with higher energy prices and health concerns, Europe’s recovery requires difficult decisions in 2022. Delayed action or lower ambitions are more likely to have higher social and economic costs in the long run. Addressing social inequalities in this sustainability transition is the key to a better future for us all.

The European Environment Agency cooperates with a large number of countries, including those in the Western Balkans. How does this cooperation further the EU’s work on the environment and how does it benefit Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia and Kosovo? We sat down with Luc Bas, head of Coordination, Networks and Strategy Programme, to discuss how the EEA is working with these countries to improve the environment.
The EEA marine assessment grid is a vector dataset based on the 'EEA reference grid'. It covers the Seas and Marine areas surrounding Europe. Open sea areas are covered by 100 km polygon grid shapes. Coastal areas are covered by 20 km polygon grid shapes. The combined EEA assessment grid fills the entire area of interest with grid cells without gaps and overlaps. Data and assessment results spatially mapped to the EEA assessment grid ensures that data can be compared in a uniform way across the European regional seas.

Besides providing trusted information on our environment and climate, the European Environment Agency (EEA) is working to improve its own environmental performance as an organisation. We interviewed Melanie Sporer who coordinates these efforts at the EEA, using the EU Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS).

The European Environment Agency’s (EEA) latest environmental performance data shows that the Agency’s work and operations in 2020 led to considerably lower impacts on the environment due mostly to restrictions imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic.

European efforts to tackle climate change, air pollution and achieving carbon neutrality were the main issues discussed during a visit of President Zuzana Čaputová of Slovakia to the European Environment Agency (EEA) on Tuesday (11 May 2021).

Efforts in tackling climate change at national level across Europe can be made more effective by robust governance frameworks as well as well-functioning, well-resourced advisory bodies. A European Environment Agency (EEA) briefing published today analyses the institutional settings for climate policy making at the national level in Europe, the role played by advisory bodies in these settings and their influence on policy decisions.

Effective action to curb climate change depends on well-defined and efficient governance systems. An increasing number of European countries have been adopting national frameworks to organise their climate actions, often in the form of climate laws. In some cases, these include dedicated advisory bodies to support policy-making. This briefing summarises key findings from research on the landscape of climate advisory bodies in European countries. It highlights the importance of ensuring the work of such bodies is effective by equipping them with a clear mandate, adequate resources and formally integrating them into regular cycles of climate policy-making, planning and progress monitoring.

The common agricultural policy is about our food, the environment and the countryside.

EC, 2015, Commission staff working document — EU assessment of progress in implementing the EU biodiversity strategy to 2020 (SWD(2015) 187 final).

EC, 2013, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions — Green infrastructure (GI): enhancing Europe’s natural capital (COM(2013) 249 final of 6 May 2013).

A good starting point to evaluate a policy is to look how others evaluated similar interventions, what are the most common elements, approaches or methodologies. Another resource to undertake policy assessment is officially reported, quality checked and publicly available information on national policies and measures.
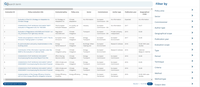
A good starting point to evaluate a policy is to look how others evaluated similar interventions, what are the most common elements, approaches or methodologies. You can find nearly 600 evaluations in the field of environment and climate policies across Europe in our catalogue.

Adapting to the impacts of climate change is a top priority in the European Union. What is driving cities to implement important measures to mitigate these impacts and make urban centres more resilient and sustainable? We sat down with Ivone Pereira Martins, EEA expert in urban sustainability on what the Agency is doing to help this vital work.
Document Actions
Share with others