When we burn fossil fuels, we release gases that create a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere, changing our planet’s climate. As a result, we experience changes to our climate (e.g. shifts in snow and rainfall patterns, rise in temperatures and other extreme climate events such as heatwaves and floods). These climate- and weather-related events also have negative impacts on our health. During the 2003 heatwave, over 70 000 fatalities were reported.
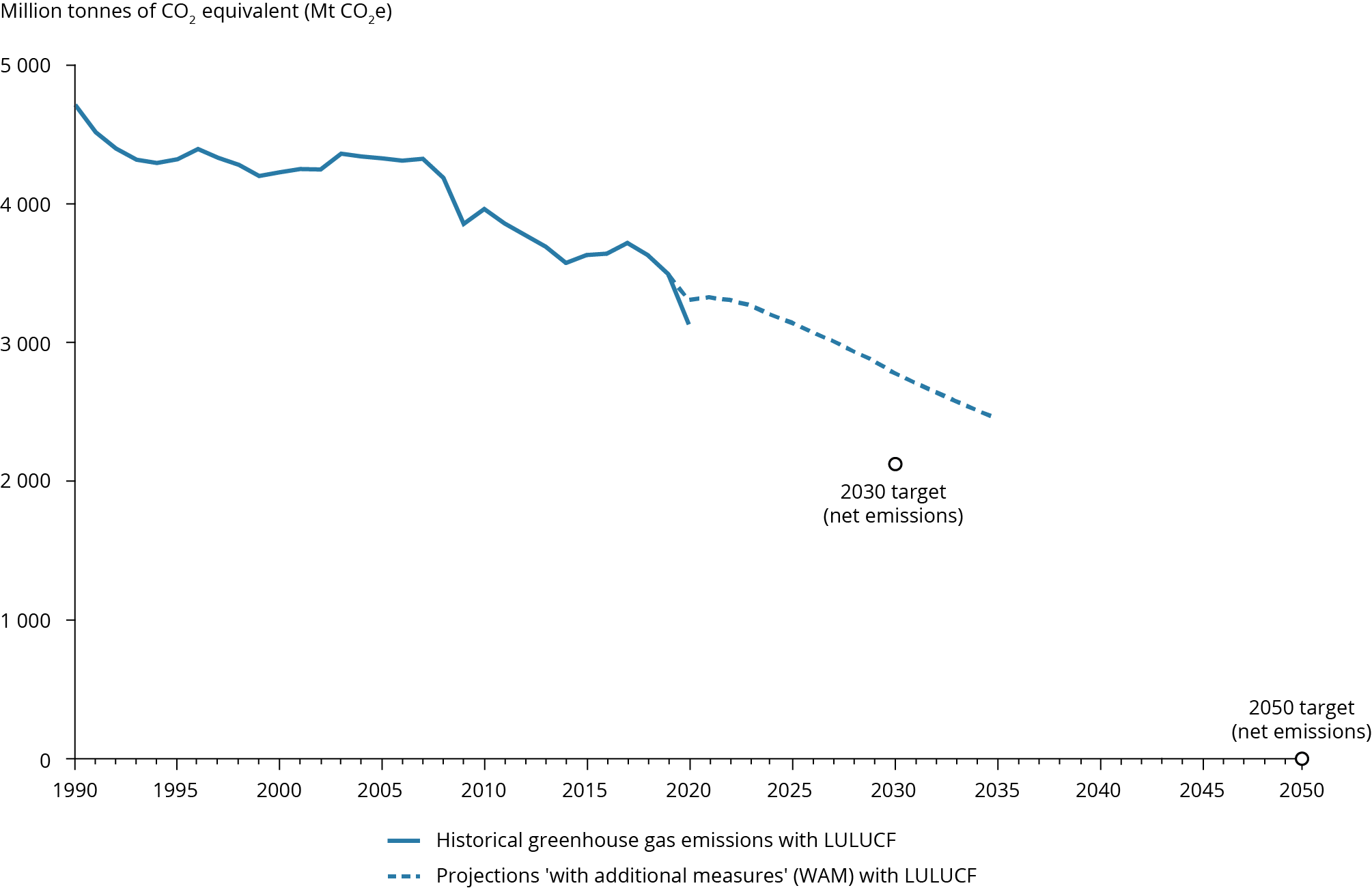
EU-27 greenhouse gas emissions in 2019 declined by 24 % compared to 1990 levels
The European Union (EU) has made good progress in reducing its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions thanks to many factors, including the implementation of EU and national policies and measures, an increase in the use of renewables, a switch from coal to gas for power generation, improvements in energy efficiency and structural changes in the EU economies. GHG emissions in the EU-27 have declined rapidly in recent years, having reached 24 % below 1990 levels and an estimated 31 % in 2020.
Source: EEA, Trends and Projections in Europe 2021, European Environment Agency.
This means that the EU has met its 2020 GHG reduction target. However, higher levels of renewables in the energy mix and energy efficiency improvements will be needed for the EU to reach its 2030 target and even more so to become climate-neutral by 2050.
Key findings from the latest analysis of greenhouse house gas emission trends:
● Greenhouse gas emissions have decreased by about one third since 1990 in the EU27, according to early estimates that also include reductions in 2020. This is mainly thanks to the implementation of EU and national policies and measures, an increase in the use of renewables, a switch from coal to gas for power generation, improvements in energy efficiency and structural changes in the EU economies.
● The EU has a set target for 2030 of a 55 % net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. According to preliminary data, the EU's net emissions in 2020 were 34 % below 1990 levels.
● Emissions have decreased in almost all sectors, particularly in energy supply, industry and the residential sector. However, emissions from transport have not fallen rapidly enough, despite climate policies and efforts to improve vehicle efficiency. Emissions from agriculture have also increased in recent years.
● Despite the good progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, substantial efforts across all the sectors of the economy will be needed to achieve a climate neutral economy by 2050 in the EU.
Read the EEA's latest report on Trends and drivers of EU greenhouse gas emissions for the complete analysis on GHG emissions
The EEA's contribution
The European Environment Agency (EEA) collects data on the annual levels of greenhouse gas emissions in European countries, analyses past and projected trends and underpinning drivers of greenhouse gas emissions, and monitors the EU’s progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By providing these data and knowledge, the EEA supports the EU in evaluating whether current policies are effective in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The EEA works closely with its member countries and the Environment Information and Observation Network (EIONET), other EU institutions (e.g. the European Commission, Eurostat and the Joint Research Centre (JRC)), experts from its European Topic Centre on Climate change Mitigation and Energy (ETC/CME), and other international organisations (e.g. the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)).

Document Actions
Share with others