
This figure combines two data sources.
The left part shows the observed change in Arctic sea ice are (individual observations and trend lines) over the period 1979 to 2023 for March (maximum ice cover) and September (minimum ice cover).
The right part shows projections of Arctic sea ice area in March and September from CMIP6 (Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6) simulations for three emissions scenarios. The thick lines denote the multimodel ensemble mean (24-27 models, depending on the scenario), and the shading shows the likely uncertainty interval (one standard deviation around the multimodel mean). The dashed line indicates a threshold for near ice-free conditions.

The figure shows the percentage point variations in the share of buses, trains, trams and metro (collective modes) and of inland waterways and trains (non-road modes) in total inland passenger and freight transport activities respectively by country.
The figure shows the share of buses, trains, trams and metro (collective modes) and of inland waterways and trains (non-road modes) in total inland passenger and freight transport activities respectively in the EU-27. For reference, the absolute activities in the EU-27 for passenger and freight transport have been included.

The figure shows the relative magnitude of emissions of pollutants from transport in EU-27 compared to 1990.

The figure shows EU-27 variations for the 1990-2021 period in the emissions of different categories of pollutants from transport by mode.

Recycling rates of municipal and packaging waste relate to waste generated. Recycling of municipal waste includes material recycling and composting/anaerobic digestion. Recycling rates of waste excluding major mineral wastes relate to waste treated. Recycling rates for waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) are calculated on the basis of the average quantity of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) put on the market in the three previous years.
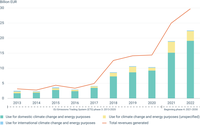
This figure presents the trends in the volume and the share of the use of EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) auctioning revenues by categories of spending.

This figure shows the trends in nitratre concentrations in European rivers and groundwater and the trends in phosphorus in European lakes and rivers

This figure shows the trends in biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and ammonium in European rivers.
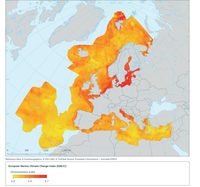
An index giving an indication of the relative magnitude of the effects of climate change stressors onmarin ecosystems.

Left graph:
A decline in pH corresponds to an increase in the acidity of ocean water.
Data originate from the Aloha station pH time series (adapted from Dore, J.E., et al., 2009, 'Physical and biogeochemical modulation of ocean acidification in the central North Pacific', Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:12235-12240).
Changes here are similar to those that are observed over a shorter time frame in Europe (see here: http://www.climatechange2013.org/images/figures/WGI_AR5_Fig3-18.jpg).
In figure, "In situ measurement (Aloha station)" corresponds to data based on in-situ measurements, while "Calculated (Aloha station)" corresponds to calculated data.
Global annual average of surface ocean pH from the Copernicus Marine Service, based on a reconstruction method using in situ data and remote sensing data, as well as empirical relationships. Indicator is available at annual resolution, and from the year 1985 onwards. The error on each yearly value varies, and is added to the data file sheet. The estimated yearly uncertainty envelope shown in the figure is defined as the annual mean of pH ± 2 standard deviations, which corresponds to a 95% confidence interval of the mean estimate.
Right graph:
Time series (1870-2022) of decadal average observed sea surface temperature anomalies (°C), with respect to the period 1991-2020, for each of the European basins, for the European seas as a whole, and for the global ocean. Data sources: HadSST4.0.1.0 (1850-2022), ERSSTTv5 (1880-2022), HadISST1 (1870-2022) and satellite-based ESA CCI/C3S SST Climate Data Record v2.1 (1991-2022).