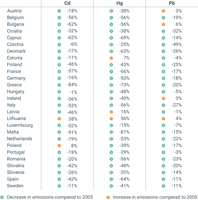
The figure shows the difference in emissions of the heavy metals between 2005 and 2022.
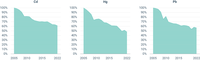
The figure shows the difference in emissions of heavy metals of individual member States in 2022 compared to 2005 levels

The figure shows the difference in emissions of the main air pollutants in 2022 compared to 2005 levels

The figure shows the actual reduction of the main air polluants by Member States from 2005 to 2022 in percentage.

The figure shows the consumption in Ozone-Depleting Potential (ODP) tonnes from 1986 to 2023

The figure shows the consumption in metric tonnes and in Ozone-Depleting Potential (ODP) tonnes from 2006 to 2023.

The figure shows the difference in emissions of Persistent Organic air Pollutants (POPs) of individual Member States in 2022 compared to 2005 levels.

The figure shows the difference in emissions of Persistent Organic air Pollutants (POPs) between 2005 and 2022.
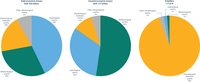
Total economic losses, insured economic losses and fatalities per hazard type.
Hazard types: meteorological hazards, hydrological hazards, climatological hazards (heat waves), climatological hazards (other).

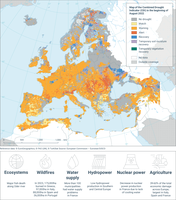
The map shows the drought situation in Europe in the first ten-day period of August 2022 (from 1 to 10 August 2022). The method is based in 6 impact levels. These levels are: "Watch" (yellow colour) when a relevant precipitation shortage is observed, "Warning" (orange) when this precipitation shortage comes with a soil moisture anomaly, "Alert" (red) when these two conditions are accompanied with an anomaly in the vegetation condition, "Temporary soil moisture recovery" (purple) when after a drought episode, soil moisture conditions went below the drought threshold but did not improve enough to consider the episode closed; "Temporary vegetation recovery" (green) when after a drought episode, vegetation conditions went below the drought threshold but did not improve enough to consider the episode closed; "Recovery" (blue) when meteorological, soil moisture, and vegetation normal conditions are recovered.
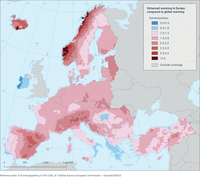
European annual mean air temperature trend (temperature regressed on time as the independent variable) expressed as multiples of the annual mean global temperature trend between 1950 and 2023, on a grid-point level.

Total number of flood events with significant socio-economic impacts by type (bar chart) and the mortality rate per year (cartogram), for the period 1870-2020.

Spatially aggregated regions for four sub-continental land and four marine regions. Regionalisation for land regions based on UN Geoscheme for Europe.

The WISE Water Framework Directive maps contain information from the River Basin Management Plans (RBMPs) reported by EU Member States, Norway and the United Kingdom according to article 13 of the Water Framework Directive (WFD). The maps include the River Basin Districts (RBDs) and their sub-units, the surface water bodies (water body category, ecological status or potential and chemical status), the groundwater bodies (aquifer type, quantitative status and chemical status) and the monitoring sites

The Quality Elements map contains information from the River Basin Management Plans (RBMPs) reported by EU Member States, Norway and the United Kingdom according to article 13 of the Water Framework Directive (WFD). The map shows the quality element status or potential for the European surface water bodies. The Quality Element status layer contains the ecological status or potential based on the quality element status value (i.e. the lowest of the known quality element status values per waterbody).

The figure shows changes in population abundance of 15 grassland butterfly species at EU level, using 1991 as reference year. The grassland butterfly index is presented as a smoothed time series and is calculated with 95% confidence limits.

The figure shows the share of bathing water of excellent quality by type and bathing season.

The figure shows the share of bathing water of excellent quality by type and country in 2023.
Document Actions
Share with others