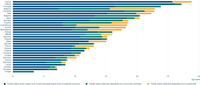
Amounts of separately collected textile waste from economic activities and households were obtained from Eurostat’s ENV_WASGEN dataset. The amounts of textile waste in mixed municipal waste are estimations based on waste composition analyses (WCAs) and calculated on the mixed municipal waste from household and similar sources. As there is no harmonised method for the WCA throughout Europe, caution should be taken when interpreting these numbers. No data available on textiles in mixed municipal waste for Türkiye. Note that, due to a lack of capacity, Ireland and Norway were not able to verify these data. Therefore data are calculated based on the residual waste composition provided in EEA’s Early Warning assessment (EEA, 2022). Italy indicated that the amount from economic activities is an overestimation as this includes non-textile waste like scraps from leather manufacturing or secondary textile waste.
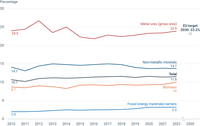
The black line indicates changes in the total circular material use rate for the EU over time, while the coloured lines show changes in the circular material use rates for the various material groups.
This data has been calculated by EEA based on Eurostat consumption trend data, EXIOBASE and the Environmental Footprint (EF). The calculations summarize the level of consumption footprint in million points (the environmental and climate impacts that result from EU citizens’ consumption) for EU27 member countries between 2010 to 2020, and the level of consumption footprint in points per capita (the environmental and climate impacts that result from EU citizens’ consumption) for EU27 member countries in 2020 compared to 2010.
The existing European Union’s (EU) monitoring framework for circular economy was established to track how the EU is transitioning to a more circular economy. To avoid unnecessary added costs and quickly establishing the EU’s monitoring framework, it has been predominantly based on existing data and covers essential elements of the transition. To complement this macro-view on how circular economy progresses in Europe, the European Environment Agency is exploring opportunities to collect new types of data generated for other purposes and, working with other partners, use them to better understand this transformation of Europe’s economy.
Document Actions
Share with others