
There must be a clear, ambitious target for cutting CO2 emissions from transport in Europe. Citizen behaviour, together with improved use of technologies, have a major role to play. These are just a few of the messages emerging from the seminar: “Right on track - choosing the most eco-friendly transport option” organised by the International Union of Railways (UIC) today at the European Environment Agency.

A preliminary analysis of data reported under the EU National Emission Ceilings Directive (NEC Directive) by Member States at the end of 2007 indicates that more countries anticipate missing one or more of their legally-binding 2010 emission ceilings compared to last year.

Emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulphur dioxide (SO2) from large combustion plants (LCP) could have been considerably lower in 2004, a report presented today by the European Environment Agency says.

High concentrations of ozone in Europe were lower during the summer of 2007 than any other year in the past decade, according to the latest data unveiled by the European Environment Agency's technical report 'Air pollution by ozone across Europe during summer 2007'. In contrast to the same season in 2006, the threshold of 180 µg/m3 was not exceeded in northern Europe.

Europe's road transport has made a clear contribution to economic growth, but its environmental performance is still unacceptable. Traffic congestion, poorer air quality, noise and in particular greenhouse gas emissions are some of the key challenges effectively addressed by six initiatives identified by the European Environment Agency as success stories. Such measures should also be implemented elsewhere, but to reach intermediate and long-term climate change targets, transport demand has to be addressed as well.

Public authorities across Europe collect a vast range of environmental data but different practices of classification and reporting make it difficult to access them and use them for cross-border analyses.

The EEA has concluded an agreement with a consortium led by the European Space Agency to provide improved information on air pollution.

A number of EU Member States are likely to miss legally-binding 2010 emission targets for four important air pollutants, according to the 'NEC Directive status report 2006' from the EEA. The report is based on the latest data officially reported by Member States under the EU National Emission Ceilings Directive (NEC Directive).

Concentrations of ozone and particulate matter, two harmful airborne pollutants, have not improved since 1997 despite substantial cuts in emissions of air pollutants across Europe, says a new EEA report, released today.

Summer ozone levels exceeded the EU’s long-term target level in 2006, threatening the health of Europeans, according to a report released today by the European Environment Agency. The frequency of ozone level exceedances was higher than in previous years, though not as high as in the record year 2003.

EPER, a register of 50 air and water pollutants' emissions produced by large and medium-sized industrial facilities in all EU Member States and Norway, was originally launched in 2004. The updated version of EPER contains data for the new EU Member States.

Emissions of sulphur (SOx) have been reduced by almost 70 % since 1990, says a new report recently released by the European Environment Agency (EEA). The report, 'Annual European Community LRTAP Convention emission inventory report 1990–2005' also shows that levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx), as reported by the EU-27 Member States, are down by 35 %.

The EU-15 can meet, and may even over-shoot, its 2012 Kyoto target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to 8 % below 1990 levels if Member States implement now all additional policies being planned, according to a new report from the European Environment Agency (EEA), released today in Copenhagen.
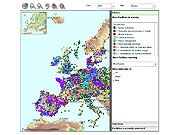
A clearer picture of the air and water pollution coming out of Europe's industrial installations is now available to the public due to improved and more complete reporting from industry. This is a key conclusion in an EPER data review report released today by the European Commission.

Greenhouse gas emissions from transport remain a key, but avoidable, obstacle to the EU reaching its Kyoto climate change targets, according to a new European Environment Agency (EEA) report, released in Copenhagen today.

Emissions of nitrogen oxides are down by 30% since the early 1990’s, according to a report released today by the European Environment Agency. The report, ‘Annual European Community LRTAP Convention emission inventory 1990-2004’ also says that emissions of sulphur (SOx) as reported by Member States dropped by 70% between 1990 and 2004 within the EU-15.

Ozone Web, a new internet tool, released in Copenhagen today by the European Environment Agency (EEA), offers users the opportunity to monitor and track ground level ozone incidents on a pan-European scale, for the first time.

Ozone Web, a new internet tool, released by the EEA today, offers users the opportunity to monitor and track ground level ozone incidents on a pan-European scale, for the first time.

Last night the European Commission and the European Environment Agency (EEA) won an award for best new electronic information source for the publication of the European Pollutant Emission Register (EPER). EPER is the first Europe-wide register of industrial emissions into air and water and was launched in February 2004. It makes detailed information on pollution from around 10,000 large industrial facilities in the EU and Norway publicly accessible on the internet for the first time. The European Information Association awarded EPER first place in its Electronic Sources Category, recognising it as the best of a large number of electronic publications, databases and websites produced at European level in 2004.

Inadequate test standards are underestimating emissions of harmful air pollutants from new cars and evidence indicates that many diesel car owners are making things worse by modifying their engines to increase power, the European Environment Agency warned today.





Document Actions
Share with others