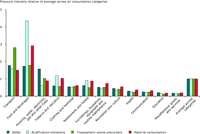
This figure compares the environmental pressure intensity of 12 different household consumption categories as defined by COICOP nomenclature i.e. the environmental pressure implications of spending one Euro on a given household consumption category compared to the average Euro spent by households.
The pressures caused by household consumption categories include both direct and indirect pressures.
Direct pressures are those released during consumption of goods and services i.e. emissions to air from cars and from burning fuels in households for heating, cooking etc. Indirect pressures caused by consumption comprise all pressures released along the production chains of consumed goods. Includes goods produced domestically and imported goods.
4 environmental pressure intensities are included – greenhouse gas emissions per Euro; acidification emissions per Euro; tropospheric ozone precursors per Euro and material consumption per Euro.
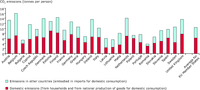
This figure identifies direct and indirect CO2 emissions caused by total national consumption in 2004 in 14 EU countries with available data for carrying out the calculations. CO2 caused by consumption are split into three components: 1) CO2 emitted abroad during the production of imported goods for direct consumption 2) CO2 emitted induced by domestic production for the home market 3) CO2 emitted directly by households through burning of fossil fuels for cooking, heating and in private cars
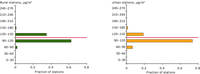
Frequency distribution of the ozone 26th highest maximum daily running 8-hour mean; the target value set in the AQ Directive is 120 ug/m3 (reference period 2008; based on all available operational ozone stations reported to AirBase)

Difference in O3 impact indicators of human health (SOMO35) (left), and ecosystems (AOT40) (right map), in 2005 as a result of the introduction of Euro vehicle emission standards in road transport
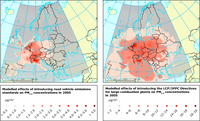
The modelled effects of introducing road vehicle emissions standards (left) and the LCP/IPPC directives for large combustion plants (right) on PM2.5 concentrations in Europe in 2005
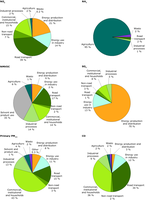
Sources of selected air pollutants in EEA-32 and West Balkan countries, 2008.
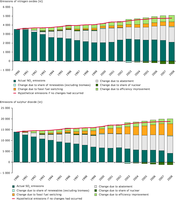
The charts show the estimated contributions of various factors affecting emissions from public electricity and heat production including public thermal, nuclear, hydro and wind plants. The top line represents the hypothetical development of emissions that would have occurred due to increasing public heat and electricity production between 1990 and 2006, if the structure and performance of electricity and heat production had remained unchanged. However, there were a number of changes to sector’s structure that tended to reduce emissions, and the contributions of each of these factors to the emission reduction are shown. The cumulative effect of all these changes was that emissions actually followed the trend shown by the lower bars.
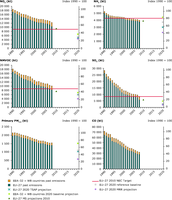
Past and projected emissions of the main air pollutants CO, NMVOC, NOx, NH3 PM2.5 and SOx
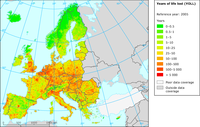
Health impact caused by exposure top PM2.5.
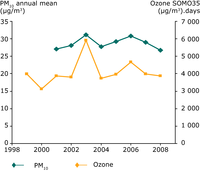
Urban air quality is of major concern. The high density of population and of economic activities in urban areas results in increased emissions, ambient concentrations and exposure. The Structural Indicator for urban air quality is presented which comprises two sub-elements describing the annual variations in population weighted health-relevant concentrations of (1) ozone and (2) particulate matter (PM10) in ambient air in urban areas.
"Annual mean concentrations of air pollutants in urban areas"
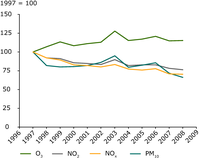
Indexed trend in annual mean urban air quality over the period 1997-2008 (reference year 1997). All urban and suburban background stations operational (that is at least reporting over 9 years with a yearly coverage of at least 274 days) during the period 1997-2008 are included. A general, Europe-wide averaged picture is shown, with a bias towards regions with high station density.
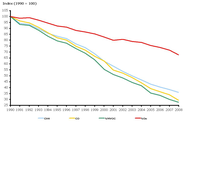
Transport emissions of ozone precursors (CH4, CO, NMVOC, NOx) in EEA member countries. The transport emissions data include all of road transport and other transport/mobile sources, less the memo items, which include international aviation (LTO (Landing and Take Off) and cruise) and international marine (international sea traffic- bunkers).
Transport emissions of emissions of primary and secondary particulates (NH3, NOx, PM10, PM2.5, SOx) in EEA member countries. The transport emissions data include all of road transport and other transport/mobile sources, less the memo items, which include international aviation (LTO (Landing and Take Off) and cruise) and international marine (international sea traffic- bunkers).
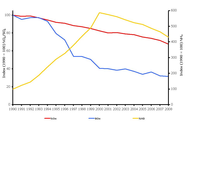
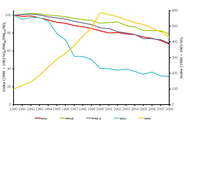
Transport emissions of acidifying substances (NOx, SOx, NH3) in EEA member countries. The transport emissions data include all of road transport and other transport/mobile sources, less the memo items, which include international aviation (LTO (Landing and Take Off) and cruise) and international marine (international sea traffic- bunkers).
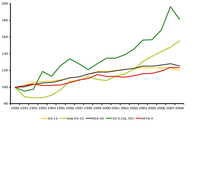
EU-15 refers to 15 old EU Member States prior to May 2004 (Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom), EFTA-3 to the three EFTA countries (Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland), New EU-12 to 12 new EU Member States as of January 2007 (Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia) and CC-2 to the two candidate countries Turkey and Iceland.
-
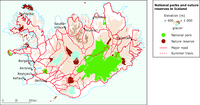
Map of Iceland showing parks/reserves, plus elevation, major roads and tracks

The maps give an overview of areas classified under Less Favoured Areas articles and mountain areas.
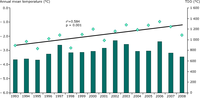
The graph shows the annual mean air temperature (black dots and regression line) and thawing degree days (TDD; bar plot), i.e. temperature sum > 0°C, from May to September at Latnjajaure, northern Sweden, during 1993–2008.
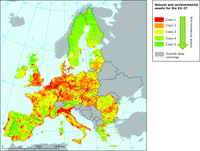
The maps show the natural and environmental assets for the EU-27.