Waterbase is the generic name given to the EEA's databases on the status and quality of Europe's rivers, lakes, groundwater bodies and transitional, coastal and marine waters, on the quantity of Europe's water resources, and on the emissions to surface waters from point and diffuse sources of pollution.
Waterbase is the generic name given to the EEA's databases on the status and quality of Europe's rivers, lakes, groundwater bodies and transitional, coastal and marine waters, on the quantity of Europe's water resources, and on the emissions to surface waters from point and diffuse sources of pollution.
Waterbase is the generic name given to the EEA's databases on the status and quality of Europe's rivers, lakes, groundwater bodies and transitional, coastal and marine waters, on the quantity of Europe's water resources, and on the emissions to surface waters from point and diffuse sources of pollution.

Percentage of water use against water availability under the temperature scenario of 3 degree increase

The European environment information and observation network (Eionet) spatial data sets include information about European river basin districts, river basin district sub-units, surface water bodies, groundwater bodies and monitoring sites. The data sets are part of the Water Information System for Europe (WISE), and compile information reported to the European Environment Agency (EEA) since 2001.
For the EEA Member countries and cooperating countries not reporting under WFD, the EIONET spatial data sets are the most up-to-date information available in WISE. The coverage is complete for Switzerland, Serbia and Kosovo and partial for the remaining countries (Liechtenstein, Turkey, Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia).
For the 27 European Union Member States, Iceland, Norway and the United Kingdom, the Water Framework Directive (WFD) reference spatial data sets are the most complete and up-to-date information available in WISE (only the EIONET monitoring sites and EIONET water bodies that could not be mapped to WFD spatial objects are included in the EIONET spatial data set).

Soil sealing is the covering of the soil surface with materials like concrete and stone, as a result of new buildings, roads, parking places but also other public and private space. Depending on its degree, soil sealing reduces or most likely completely prevents natural soil functions and ecosystem services on the area concerned. Particularly in urban areas, soil is being sealed off with increasing housing and infrastructure. This dashboard give insight into loss of estimated carbon sequestration and water holding capacity due to sealing.

• Total water input is expressed in m3/ha and gross value added is expressed in purchasing power standard (PPS)/ha, where the area in ha represents the sum of arable land and land with permanent crops. The monetary unit being used (PPS) accounts for purchasing power differences among countries. Theoretically, one PPS can buy the same amount of goods and services in each country.
• Water use intensity of crop production is classified at the regional level according to the quartile (Q) distribution of all time series (2005-2016): below Q1 (light blue) indicates a low water intensity of crop production; above Q3 (dark blue) indicates a high water intensity of crop production; and between Q1 and Q3 (mid-blue) indicates a moderate water intensity of crop production.
• Regional groupings of EU Member States and the UK are based on UN Geoscheme — Standard M49: eastern Europe (Bulgaria, Czechia, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Slovakia), northern Europe (Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Ireland, Lithuania, Latvia, Sweden and the United Kingdom), southern Europe (Cyprus, Greece, Croatia, Italy, Malta, Portugal, Slovenia and Spain) and western Europe (Austria, Belgium, Germany, France, Luxembourg and the Netherlands).
• Gap filling has been performed for certain years and countries: 2010 data have been used for 2011 Greece data; 2006 data have been used for 2007 Hungary data; 2005 data have been used for 2007 Luxembourg data; 2009 data have been used for 2010 Portugal data; 2015 data have been used for 2016 Sweden data.
This raster dataset represents the probability of occurrence of whales in the Europe Seas, where the species included are: Blue whale, Sei whale, Humpback whale, Sperm whale, Fin whale and Northern right whale.
This raster dataset represents risk of collision of whales with vessels in the Europe Seas. Species included are: Blue whale, Sei whale, Humpback whale, Sperm whale, Fin whale and Northern right whale.
The northern right whale model only describes the range of the western population of this species, since the eastern population is probably almost extinct. Thus, the northern right whale model only partly overlaps with the EEA area on interest.
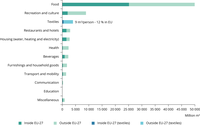
To produce and handle all clothing, footwear and household textiles purchased by EU-27 households in 2020, an estimated 4024 million m³ of blue water was used (9m³ per person), making this consumption domain the third highest impact category after food and recreation. Only 12% of blue water consumption takes place within Europe.
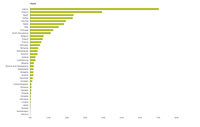
WEI+ illustrates the percentage of water use against renewable freshwater resources in a given time and place
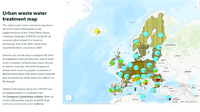
The urban waste water treatment map shows the most recently reported information on the implementation of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD). It is based on data from 2020 in EU-27 (2020) countries plus Iceland, which were reported by countries in 2022. Data are provisional, pending compliance assessment by the European Commission.
The Water Framework Directive (WFD) protected area data sets include information about European drinking water protected areas, designated waters such as fish protected areas and shellfish protected areas, nitrates vulnerable zones, urban waste water sensitive areas and bathing water protected areas.
The protected areas are part of the Water Framework Directive register of protected areas and were reported in second River Basin Management Plans (RBMP) or under other related reporting obligations.
The data sets are part of the Water Information System for Europe (WISE), and compile information reported by the EU Member States, Albania, Iceland, Norway, Montenegro, Switzerland and the United Kingdom to the European Commission (EC) and the European Environment Agency (EEA).
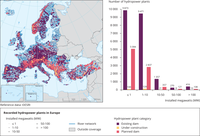
The figure shows the number of existing, under construction and planned hydropower plants by size categories (installed megaWatts) in Europe.
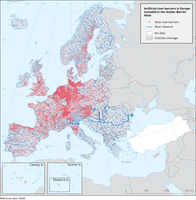
The figure shows a compilation of 630,000 unique barrier records from existing datasets.
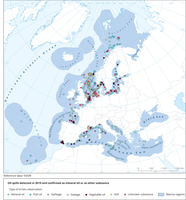
The map shows the mineral oil and other substance detections confirmed by CleanSeaNet users in 2019 as inserted into the system by 07 Januray 2020

The left map shows the ship density of the Baltic Sea based on AIS and VMS data. The colour scale is presented in log10 for clarity. The data is for the whole year of 2014 and includes all categories of ships. The right map shows the median value of the sound pressure level for the 125 Hz 1/3-octave band. Elevated sound pressure levels are noted in the red areas where the shipping density is high. The sound pressure level was determined as an average over the entire water column.

The Water Framework Directive aims to achieve good status for all rivers, lakes and transitional and coastal waters in the EU. Achieving good ecological status for surface waters is critical to this. According to countries’ second river basin management plans, good ecological status had been achieved for around 40% of surface waters (rivers, lakes and transitional and coastal waters) by 2015. However, these plans show only limited improvement in ecological status since the first plans were published in 2009, with ecological status remaining similar for most water bodies.

Ocean surface pH declined from 8.2 to below 8.1 over the industrial era as a result of an increase in atmospheric CO 2 concentrations. This decline corresponds to an increase in oceanic acidity of about 30%. Reductions in surface water pH are observed across the global ocean. Ocean acidification has impacts on marine organisms and has already affected the deep ocean, particularly at high latitudes. Models project further ocean acidification worldwide. The target under United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 14.3 is to minimise the impacts of this by 2030.
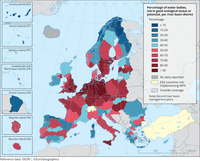
The map presents the proportion of surface water bodies (rivers, lakes, transitional and coastal waters) in less than good ecological status per River Basin District.
Document Actions
Share with others