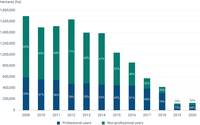
This figure shows the use of plant protection products by professional and non-professional users by year in non-agricultural areas in France. More precisely, it shows the evolution, calculated only for non-agricultural areas, of an indicator known as NODU («Nombre de Doses Unités»). The non-agricultural NODU corresponds to the surface area of gardens, green spaces and infrastructures (so-called JEVI) that would be treated annually with the plant protection products sold during the course of a year, at the maximum authorised doses. After a period of strong decrease, the 2020 non-agricultural NODU stands at 130,736 ha in 2020, down 92% since 2009. As a result of the use restrictions applied to private individuals in France, the share of non-professional use in the 2020 non-agricultural NODU is decreasing: it goes from 65% (1,104,758 ha) in 2009 to 32% (41,953 ha) in 2020.

The vertical bars represent the time-weighted mean concentration of active substances as measured during the period May to September of each year between 1992 and 2018 (except only May to June in 1993). The dots represents the total amount of active substances (of those analysed) that were applied on field in the Vemmenhög area during the same period (1992-2018). The two vertical lines show that the first significant reduction in the concentration of active substances occurred in 1995, following the onset of the provision of site-specific guidance to farmers on how to prevent the release of pesticides to local surface waters. The second fall in pesticide levels was seen in 1998, after the implementation of economic incentives by the government and industry.
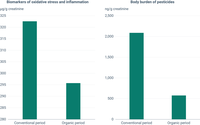
The two charts illustrate some of the results of the randomised clinical trial which was conducted in Cyprus as part of the “Organic diet and children’s health” study. In the study, urine samples from children aged 10-12 from schools in the Limassol area of Cyprus were analysed during two separate periods. During a 'conventional' period, participants were asked to maintain their usual dietary choices (>80% conventional diet) for a total of 40 days. During the 'organic period', participants were asked to follow strictly the two ~20-day sequential organic dietary menus provided to them for 40±3 days. Two urinary biomarkers were then measured by the researchers. The first were biomarkers of exposure to pyrethroid pesticides (3-phenoxybenzoic acid, 3-PBA), and neonicotinoid pesticides, (6-chloronicotinic acid, 6-CN). The second were biomarkers of oxidative stress/inflammation (8-iso-prostaglandin F2a [8-iso-PGF2a], malondialdehyde [MDA], and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine [8-OHdG]), which are considered as early-stage indicators for chronic conditions, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes or cancer. The left chart shows the measurements for the urinary biomarkers of oxidative stress/inflammation (8-OHdG), while the right chart shows those for the urinary biomarkers of pyrethroid pesticides (3-PBA). The results illustrate that the children had a lower body burden of pyrethroid pesticides and lower levels of oxidative stress/inflammation biomarkers during their 'organic period'. These results were statistically significant.

The maps show the monitoring sites in Europe that exceeded effect or quality thresholds for (left) imidacloprid in surface waters (right) atrazine in groundwater in the year 2020. The classification of 'unknown’ for some monitoring sites means that the substance was detected but the concentration was below the limit of quantification (LoQ) and the LoQ was higher than the assessment threshold. This means that it is impossible to determine whether there was an exceedance or not. The data reported for imidacloprid in surface waters cover 16 countries. The data reported for atrazine cover 18 countries. The monitoring results are reported under the Water Information System for Europe State of Environment (WISE SoE) reporting, more specifically WISE 6, and the spatial data for the monitoring sites are reported under the Water Framework Directive and the WISE 5 Spatial data reporting.
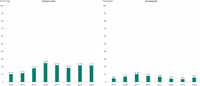
The figures show the percentage of monitoring sites with exceedance of effect thresholds or quality standards, set by European or national regulatory standards, and weighted by country area to reduce the impact of uneven data reporting (2013-2020). For surface waters, EU environmental quality standards and (in the absence of those) national regulatory standards were used, reflecting the lowest ecotoxicologically-based effect threshold. Effect thresholds were identified for 120 out of 248 pesticides (48%). The exceedances included here refer to those 120 pesticides. For groundwater, the Groundwater Directive quality standard of 0.1µg/l was used to identify exceedance. Twelve non-relevant metabolites (nrM) were excluded from the assessment.
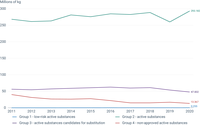
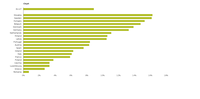
The chart shows the total amount (in kilograms) of active substances sold in the EU-27 annually between 2011 and 2020, by categorisation of active substances. The statistics on quantities of active substances placed on the market in plant protection products are collected under Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009, provided to Eurostat under Annex I of Regulation (EC) No 1185/2009 on statistics on pesticides. These are are also disseminated in the Eurostat dataset ‘Pesticide sales’ (aei_fm_salpest09).Those data are categorised into 4 groups defined in the Annex of Commission Directive (EU) 2019/782.The categorisation of active substances is the same as the one used by the European Commission for the calculation of its harmonised risk indicators. It includes: group 1 - low-risk active substances; group 2 – approved active substances; group 3 - active substances that are candidates for substitution and group 4 - unapproved active substances. Goup 2 includes approved active substances that are neither low-risk nor candidates for substitution, around 75% of all approved active substances in the EU according to the EU Pesticides Database.

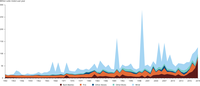
Country data from European database on disturbances

Deforestation in the EU-27 as collected by countries for the reporting on forest resources to the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and Forest Europe processes
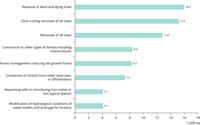
The eight most relevant pressures on forests from forestry activities.
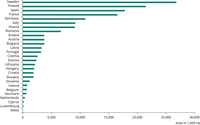
Forest area in the EU-27 as collected by countries for the reporting on forest resources to the UNECE, FAO and Forest Europe processes
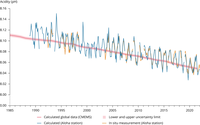
A decline in pH corresponds to an increase in the acidity of ocean water. Data originate from the Aloha station pH time series (adapted from Dore, J.E., et al., 2009, 'Physical and biogeochemical modulation of ocean acidification in the central North Pacific', Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:12235-12240). Changes here are similar to those that are observed over a shorter time frame in Europe (see here: http://www.climatechange2013.org/images/figures/WGI_AR5_Fig3-18.jpg). In figure, "In situ measurement (Aloha station)" corresponds to data based on in-situ measurements, while "Calculated (Aloha station)" corresponds to calculated data.
Global annual average of surface ocean pH from the Copernicus Marine Service, based on a reconstruction method using in situ data and remote sensing data, as well as empirical relationships. Indicator is available at annual resolution, and from the year 1985 onwards. The error on each yearly value varies, and is added to the data file sheet. The estimated yearly uncertainty envelope shown in the figure is defined as the annual mean of pH ± 2 standard deviations, which corresponds to a 95% confidence interval of the mean estimate.
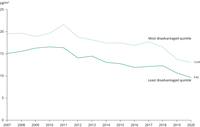
The figure shows the annual average population weighted concentration of PM₂.₅ in the poorest quintile (upper line) and richest quintile (lower line) of NUTS3 regions in the EU, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita at purchasing power standard.
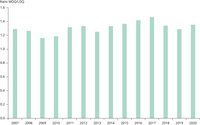
The graph shows the ratio of the annual average population weighted concentration of PM₂.₅ in the poorest quintile divided by that of the richest quintile of NUTS3 regions in the EU, as measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita at purchasing power standard, per year.