The European forest types — Categories and types for sustainable forest management reporting and policy presents the findings of a study carried out by an international consortium of experts aimed at providing the Ministerial Conference on the Protection of Forests in Europe (MCPFE) with an user‑friendly forest types classification. The primary goal of the scheme is to improve the MCPFE reporting on sustainable forest management (SFM) in Europe, with special regard to forest type based SFM indicators.

This report assesses farmland, forests, freshwater
ecosystems, marine and coastal systems, wetlands of
international importance and mountain ecosystems
in order to provide evidence of progress — or lack
of progress — towards the 2010 target of halting the
loss of biodiversity.
The Corine biotopes shape files and database is an inventory and location of major nature sites in the Phare countries (Albania, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia). The database is part of the Corine biotopes project to enhance reliable and accessible information about vulnerable ecosystems, habitats and species of importance as background information for Community environmental assessment.

Recent analyses by the EEA show that land is becoming a scarce resource: 800 000 ha of Europe's land cover was converted to artificial surfaces from 1990-2000. Only with careful spatial planning of urban and rural development can Europe avoid compromising its agricultural production, biodiversity, energy security and Kyoto targets and aspirations under the Lisbon agenda.

The European Union will not reach the goal of halting species loss by 2010 if it does not do more to prevent the decline of its most nature-rich areas of farmland, the European Environment Agency (EEA) and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) warned today.

Stakeholders' Conference - Biodiversity and the EU - Sustaining Life, Sustaining Livelihoods
NOTE: In 2010, the Natura 2000 database was published and is available for download from this site. The Areas of high ecological value is outdated and should not be used.
The Corine biotopes (Version 2000) database is an inventory of major nature sites

Towards an urban atlas: Assessment of spatial data on 25 European cities and urban areas

This report describes both the eleven biogeographical regions and the seven regional seas around Europe in comparable chapters. The main focus of the chapters is on wild-living species, on the major ecosystems and some selected natural or semi-natural habitat types. The geographical coverage of the report is Europe to the Urals with surrounding regional seas.
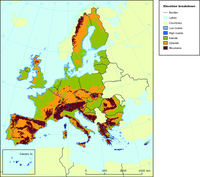
The Elevation breakdown is used to allocate land cover changes into homogeneous areas as function of height, slope and distance to the sea

!



Document Actions
Share with others