Discharges from urban areas are the largest, but not the only contributor of orthophosphate pollution to water. Phosphorus concentrations generally decreased in European rivers and to a lesser extent lakes during the 1990s, reflecting the improvement in wastewater treatment during this period.
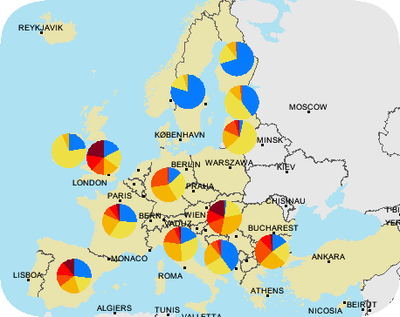
The map shows pie charts of the mean annual concentrations of orthophosphate measured at Eionet-Water River monitoring stations in 2005 aggregated at country level. The size of each segment of the pie charts is proportional to the number of stations with orthophosphate concentrations falling within defined concentration limits. The segments are coloured according to the different concentration levels.

Click on the map icon to see the WISE map of
phosphate concentration of rivers of the European countries
Document Actions
Share with others