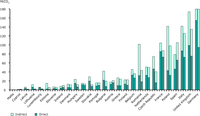
The figure shows the CO2 emissions in the industry in EU Countries

The figure displays the unit energy consumption per ton of paper as a function of the ratio pulp production to paper production: the higher the ratio, the higher the energy unit consumption.

Figure compares the energy unit consumption of cement in EU countries as a function of the share of clinker: the higher this ratio, the higher the specific energy consumption.
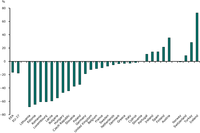
Based on the ratio : energy consumption / population (%/year calculated on the period 1990-2008)

Energy efficiency index of industry (ODEX) is a weighted average of the specific consumption index of 10 manufacturing branches; the weight being the share of each branch in the sum of the energy consumption of these branches in year t and the sum of the implied energy consumption from each underlying industrial branches in year t (based on the unit consumption of the sub-sector with a moving reference year).

Figure shows a more detailed comparison of the performance (in terms of energy unit consumption) of the European steel sector across the different EU-27 countries taking into account the relative share of electric steel in total crude steel production.
Energy efficiency index of industry (ODEX) is a weighted average of the specific consumption index of 10 manufacturing branches; the weight being the share of each branch in the sum of the energy consumption of these branches in year t and the sum of the implied energy consumption from each underlying industrial branches in year t (based on the unit consumption of the sub-sector with a moving reference year).
Based on the ratio: energy consumption by end uses divided by the number of permanently occupied dwelling.

The energy consumption of households is decomposed in different explanatory effects: change in average dwelling size, increasing number of appliances (more electrical appliances) and central heating diffusion, energy efficiency improvement (as measured from ODEX) and change in behaviour related to more confort.

Variations in CO2 emissions from household and the explanatory effects.

The unit consumption in useful terms is calulated by multiplying the final consumption for each fuel by the heating efficiency for that fuel.
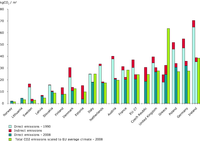
The graph compares by country the level of CO2 emissions for space heating per m2 for 2 years : 1990 and 2008 (direct and indirect emissions).
1990 and 2008 data are climate corrected against each country’s long-term average climate, whereas the last series is climate corrected and scaled against the EU long-term average climate to account for temperature differences between countries.
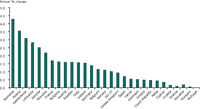
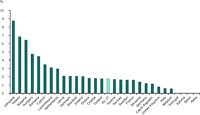
Change in energy efficiency index by country in the period 1997-2008

CO2 emissions per dwelling: direct and indirect emissions
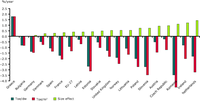
Unit consumption for households can be expressed in energy consumed per dwelling (toe/dw) or energy consumed per floor area (koe/m2). The floor area per dwelling for EU27 is extrapolated from the weighted average floor area of dwellings of 19 countries (9 EU-15 countries and 10 new members) which represent around 85% of the total EU stock of dwellings; the weighting factor is the stock of dwellings.
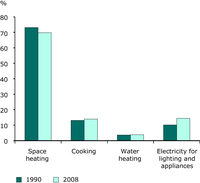
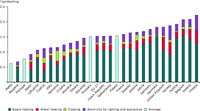
Share of energy consumption by end uses in total households consumption.

Influence of climate on household energy consumption per dwelling between 1990 and 2008.
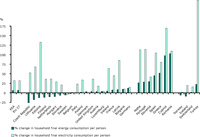
Based on the ratio : energy consumption / population (%/year calculated on the period 1990-2008)
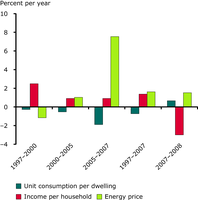
The graph characterizes the average consumption per households (at normal climate) in relation to the evolution of prices and incomes. The income per households for EU-27 as a whole is the sum of the 27 EU countries based on national Odyssee data.
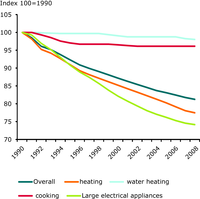
For households, the ODEX is carried out at the level of 3 end-uses (heating, water heating, cooking) and 5 large appliances (refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers and TVs)