
Since 1990, emissions of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) decreased in the EEA-33 countries, e.g. hexachlorobenzene (HCB) decreased by 95 %, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by 75 %, dioxins and furans by around 70 % and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by 83 %.
The majority of countries report that POP emissions fell during the period 1990 to 2017.
In 2017, the most significant sources of emissions included the ‘Commercial, institutional and households’ and ‘Industrial processes and product use’ sectors.

The maps shows the changes relative to present in irrigated and rain fed yields between 2021-2014 compared to 1981-2010 for wheat, maize and sugar beat. Left side shows irrigated - and right side shows rain fed for RCP8.5, per NUTS2 region. Wheat in Europe is not irrigated.
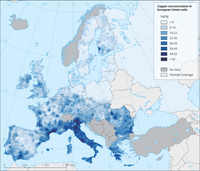
Map of Copper concentrations in European Union agricultural top soils (upper 20 cm).
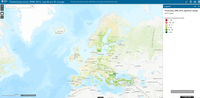
This interactive viewer shows land recycling status and change accounts for major European Functional Urban Areas (FUAs). Land recycling addresses the reuse of abandoned, vacant or underused urban land for new developments. Land recycling is considered a response to land take within FUAs, i.e. urban development on arable land, permanent crop land or semi-natural areas. It is a key planning instrument for achieving the goal of no net land take by 2050 (EC, 2016).

The intensity of land take is calculated as land take in the given period as a percentage of the area of artificial surfaces in 2000. For easier comparability, land take is summarised within NUTS3 regions.
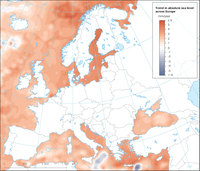
Spatial distribution of trends in mean sea level in European seas (January 1993- December 2017)
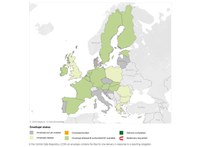
Article 12 of the Birds Directive requires Member States to report about the progress made with the implementation of the Directive. A report is sent to the European Commission every 6 years following an agreed format. These scoreboards provide information on timeliness of data delivery by Member States for the reporting 2013-2018.
These data sets show the European forest area in 2012 and in 2015 at 100m spatial resolution, covering EEA39 countries. They are based on Copernicus HRL forest products at 20m spatial resolution and comply with the FAO forest definition (i.e. minimum mapping unit of 0.5 ha, minimum coverage of 10% and excluding land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban land use).
After the selection of those pixels identified as forest by the HRL forest products and also compliant with FAO criteria, the forest area dataset at 100m was computed as a Boolean product (i.e. forest / non-forest). The value 1 (forest area) correspond to the pixels where forest is the major coverage; otherwise the pixel value is 0 (non-forest area).
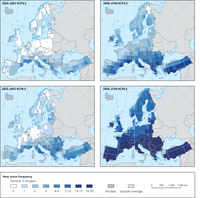
The top maps show the median of the number of heat waves in a multi-model ensemble of the near future (2020–2052) and the latter half of the century (2068–2100) under the RCP4.5 scenario, and the lower maps are for the same time periods but under RCP8.5
The delineation of European mountain areas was carried out by using digital elevation models, considering different criteria combination of thresholds of altitude, climate, and topography variables (IP2008 8.2.7 Regional and territorial development of mountain areas, ETC/LUSI - EEA). This dataset was created in 2008, covers the full European continent and is a reference layer for the EEA Report No 6/2010 on Europe's ecological backbone: recognising the true value of our mountain.
The present 100m raster datasets are the CORINE Land Cover status layers for 2000, 2006, 2012 and 2018, modified for the purpose of consistent statistical analysis in the land cover change accounting system at EEA.
CORINE Land Cover (CLC) data are produced from 1986 for European (EEA member or cooperating) countries. Altogether five mapping inventories were implemented in this period, producing five status layers (CLC1990, CLC2000, CLC2006, CLC2012, CLC2018) and four CLC-Change (CLCC) layers for the corresponding periods (1990-2000, 2000-2006, 2006-2012, 2012-2018). Pan-European CLC and CLCC data are available as vector and raster products.
Due to the technical characteristics of CLC and CLCC data, the evolution in CLC update methodology and in quality of input data, time-series statistics derived directly from historical CLC data includes several inconsistencies. In order to create a statistically solid basis for CLC-based time series analysis, a harmonization methodology was elaborated.
