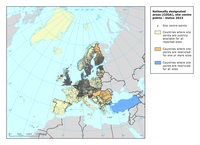
The map shows the CDDA site centre points and countries where site centre points are public available, countries where some site centres are having restrictions and countries where site points have restrictions for all sites

Data compiled by EEA. At EU level, the data provided are total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (excluding emissions from LULUCF, including emissions from international aviation), which are consistent with the emission scope covered in the EU’s objective to reduce its GHG emissions by 20% compared to 1990 by 2020. At Member State level, the data provided are ‘non-ETS emissions’ (emissions covered under the ‘Effort Sharing Decision’ (406/2009/EC)). The Effort Sharing Decision sets national annual binding targets for emissions not covered under the EU emission trading scheme (ETS). These non-ETS emissions exclude emissions from LULUCF, emissions from international aviation and CO2 emissions from domestic aviation.
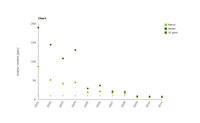
EU-27 unweighted average sulphur content of road transport fuel, 2001 - 2011
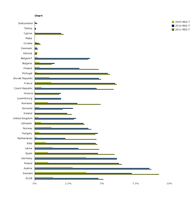
% share of renewable energy consumption in transport by EU-28 member country, including all biofuels consumed in transport
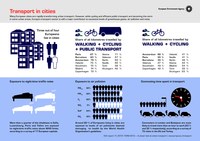
Many European cities are rapidly transforming urban transport. However, while cycling and efficient public transport are becoming the norm in some urban areas, Europe’s transport sector is still a major contributor to excessive levels of greenhouse gases, air pollution and noise.
EEA

Emission levels are not the only factor that determines concentrations of air pollutants. Factors like the weather, chemical transformations in the air, and transport of pollutants from outside Europe all play a role. This means that a reduction in emissions of a pollutant do not always translate to an equivalent reduction in concentrations of that pollutant.

Air pollution impacts human health, contributes to climate change and damages ecosystems. Here are some of the pollutants the ‘Air quality in Europe – 2013 report’ investigates and their potential impacts.
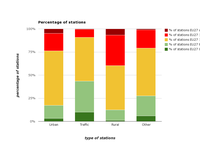
Distribution of stations by thresholds of the 93.15 percentile of the daily maximum of the running 8-h mean O3 concentrations for the year 2011. The chart is based on the 93.15 percentile of the daily maximum of the running 8-h mean O3 concentrations, corresponding to the 26th highest O3 concentration when data availability is 100% over the year.
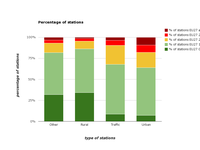
Distribution of stations by thresholds of PM2.5 annual mean concentrations for the year 2011.
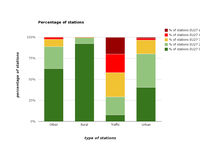
Distribution of stations by thresholds of NO2 annual mean concentrations for the year 2011.
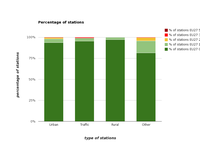
Distribution of stations by thresholds of 99.73 percentile of the hourly SO2 concentrations for the year 2011. The chart is based on the 99.73 percentile of the SO2 hourly concentrations, corresponding to the 25th highest SO2 concentration when data availability is 100% over the year.

Distribution of stations by thresholds of CO maximum daily max 8-hour mean for the year 2011.
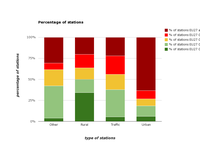
Distribution of stations by thresholds of benzo(a)pyrene annual mean concentrations for the year 2011.
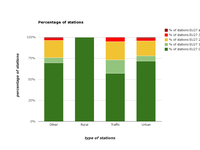
Distribution of stations by thresholds of C6H6 annual mean concentrations for the year 2011.
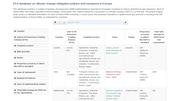
This database contains a number of policies and measures (PAM) implemented or planned by European countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Most of these PAMs have been reported to the European Commission, the United Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) or the EEA. The search engine gives access to detailed information for each of these PAMs including, in some cases, the expected reductions in greenhouse gas emissions resulting from the implementation of these PAMs, as estimated by countries.

Line graph of changes over time in consumption per capita for poultry, cheese, fish and seafood, milk, meat, pork and beef (index: 1995 = 100)



