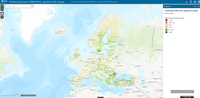
This interactive data viewer provides a set of dashboards giving an overview of the land take and net land take processes for Europe (EEA39 and EU28) derived from the CORINE land cover data series. Statistics are derived for every 6 years of the acquisition period, as well as for the entire period (2000-2018). The viewer facilitates the assessment of land take over a specific period as well as the land use drivers of the observed changes, which can be analyzed within user defined spatial units such as administrative regions, biogeographical regions or land cover classes.
This dataset refers to the Richness index of Species and Habitats of Conservation Concern indicator. This indicator has been developed to be used as a sub-indicator for contributing to the identification of the High Nature Value (HNV) Forest Areas as it will be integrated with other sub-indicators of horizontal structure, management and naturalness to generate the final composite indicator. It is composed itself of three sub-indicators: “Forest Non-bird species”, “Forest bird species” and “Forest habitats”. All the three sub-indicators build on distribution data from the reporting of habitat and species conservation status under Article 17 of the Habitats Directive and Article 12 of the Birds directive which describe their distribution at 10km grid resolution. The forest species and the forest habitats proposed to be used for the HNV forest area identification were selected based on expert judgement (ETC/BD) and raster files reporting the count of forest species and habitats were created. At this stage, no weight is applied based on Habitat and Species prioritization, conservation status or endemism. The sub-indicators were then normalized for each European forest type and successively combined not assigning any specific weight to a particular sub-indicator.
The values for this indicator, present in this dataset, ranges between 0 and 1. The values close to 1 mean high presence of habitats and species related to forest, whereas the lower richness are closer to 0. It covers the forested areas of the EU27 Member States except for Cyprus (data from Croatia will be reported starting from the next update regarding the period 2013-2018).
Forest management involves various degrees of human intervention to safeguard the forest ecosystem and its functions as well as the exploitation of forest resources. While the objectives of management vary widely and include the protection of resources in protected forests and nature reserves, the primary objective is mostly the production of wood products. Although sustained yield forestry continues to be widely practised, there is an increasing trend towards the management of forests as ecological systems with multiple economic benefits and environmental values, ensuring that benefits meet present as well as future generations’ needs. In order to assess forest management intensity in Europe an indicator based on three data sources has been developed: a) Fast track ecosystem capital accounts (forest growth & harvest – disaggregated to 1km grid), b) Potential forest management (gradient of intensity of intervention with the natural processes in a forest) c) Forest fragmentation (forest ecosystem network connected by forest bridges – GUIDOS Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis).
Each input dataset has been assessed separately in a first step in terms of pressures on forest ecosystems which are the result of the specific management, use or respectively state of the forest patch. The overall management related pressure is then derived by crossing the relative pressures by each input and evaluating the constellation of the input representative factors.
This updated version of the management related forest pressures is based on the first assessment done in framework of the ETC-SIA report "Land use and land management related pressures on agricultural and forest ecosystems" (ETC-SIA, Task 1.8.4.3 Ecosystem pressures).
The natural assemblage species indicator dataset is a forest dataset that measures the congruency between the potential and current tree species distribution. The natural assemblage indicator is considered one of the key indicator for the identification of High Nature Value forest area in Europe. The reference year for this data set is 2006 and the spatial coverage is including the 28 EU Member States, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, and Turkey.
The methodological approach is based on two data sources: (1) EUNIS woodland, forest and other wooded land habitats, predicted potential distribution of habitat suitability –EEA- as potential distribution; (2) Relative probability of presence of forest tree species (RPP) of European Atlas of Forest Tree Species –JRC- as current distribution.
The dataset values express, in the fuzzy values between 0 and 1, the percentage of tree species vegetation agreed with potentially dominant tree species by pixels. This measure is independent of the current forest coverage. The values close to 1 mean high percentage of native tree species (natural) whereas values close to 0 are an approximation of a low level of naturalness, being a high percentage of non-native species.


Since 1990, emissions of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) decreased in the EEA-33 countries, e.g. hexachlorobenzene (HCB) decreased by 95 %, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by 75 %, dioxins and furans by around 70 % and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by 83 %.
The majority of countries report that POP emissions fell during the period 1990 to 2017.
In 2017, the most significant sources of emissions included the ‘Commercial, institutional and households’ and ‘Industrial processes and product use’ sectors.

The maps shows the changes relative to present in irrigated and rain fed yields between 2021-2014 compared to 1981-2010 for wheat, maize and sugar beat. Left side shows irrigated - and right side shows rain fed for RCP8.5, per NUTS2 region. Wheat in Europe is not irrigated.
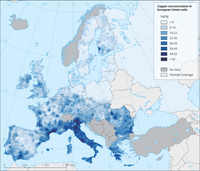
Map of Copper concentrations in European Union agricultural top soils (upper 20 cm).
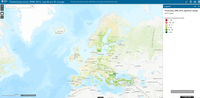
This interactive viewer shows land recycling status and change accounts for major European Functional Urban Areas (FUAs). Land recycling addresses the reuse of abandoned, vacant or underused urban land for new developments. Land recycling is considered a response to land take within FUAs, i.e. urban development on arable land, permanent crop land or semi-natural areas. It is a key planning instrument for achieving the goal of no net land take by 2050 (EC, 2016).

The intensity of land take is calculated as land take in the given period as a percentage of the area of artificial surfaces in 2000. For easier comparability, land take is summarised within NUTS3 regions.
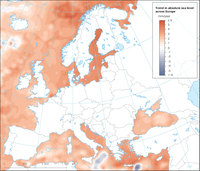
Spatial distribution of trends in mean sea level in European seas (January 1993- December 2017)
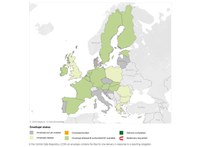
Article 12 of the Birds Directive requires Member States to report about the progress made with the implementation of the Directive. A report is sent to the European Commission every 6 years following an agreed format. These scoreboards provide information on timeliness of data delivery by Member States for the reporting 2013-2018.
These data sets show the European forest area in 2012 and in 2015 at 100m spatial resolution, covering EEA39 countries. They are based on Copernicus HRL forest products at 20m spatial resolution and comply with the FAO forest definition (i.e. minimum mapping unit of 0.5 ha, minimum coverage of 10% and excluding land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban land use).
After the selection of those pixels identified as forest by the HRL forest products and also compliant with FAO criteria, the forest area dataset at 100m was computed as a Boolean product (i.e. forest / non-forest). The value 1 (forest area) correspond to the pixels where forest is the major coverage; otherwise the pixel value is 0 (non-forest area).