Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 17 Feb 2025
Most of the land‑based species have colonised Iceland from northwestern Europe during the postglacial time, or in the last 11 000 years. About one-third of the vascular plants may be characterised as Arctic-Alpine, while about half of the species are Boreal. Endemic species are few and there are only two known species of chironomids (1) and two known species of subterranean freshwater amphipods in Iceland. In addition, some geothermal microorganisms are only found in Iceland (2). A small number of species has been explained by climate and isolation i.e. a long distance from continental Europe (3). Contrary to the land, the marine biota is characterised by species richness and high productivity. Iceland is on a crossroads between east and west and Arctic and the temperate latitudes (2). The number of species found in Iceland within selected groups of organisms is shown in figure 1.
|
Groups of organisms
|
Number of species
|
|
Mammals
Land (7) and sea mammals
|
26
|
|
Birds
Nesting birds
|
76
|
|
Fish
Fresh water (7) and marine species, within the economic zone
|
340
|
|
Insects
|
ca. 1290
|
|
Arachnid
Acari not included
|
96
|
|
Molluscs
Clams and snails
|
ca. 500
|
|
Other invertebrates
Such as Hydrozoa, Echinoderms, Polychaeta, Nematoda et.c.
|
ca.1700
|
|
Vascular plants
Angiosperms and ferns
|
485
|
|
Moss
|
606
|
|
Lichen
|
830
|
|
Algae
|
500
|
|
Fungi
|
1880
|
Figure 1. Number of species within selected organism groups.
Nature conservation
Almost 100 sites, with a total area of 2 000 000 ha (in this figure, glaciers and marine areas are included) (Figure 2), are protected in Iceland under the terms of Nature Conservation act, or by other laws.
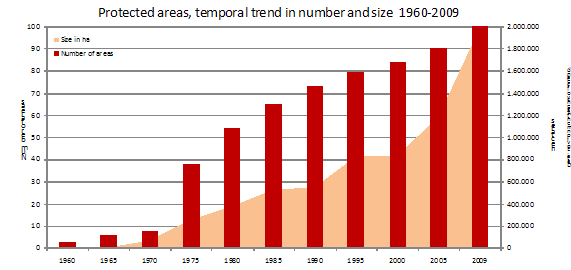
Figure 2. Trend in number and total size of protected areas in Iceland since 1960.
Protected areas for Nature Conservation are classified as National Parks, Nature Reserves, Natural monuments on land and at sea, Country parks and Areas protected by special law.
Nature Reserves
Nature reserves may be established in areas considered important of their landscape, flora or fauna.
National Parks
National parks may be established in areas considered outstanding in landscape, flora or fauna, or having special historic significance.
Natural monuments on land and at sea
Natural monuments are natural phenomena that are unique, of outstanding beauty or scientific interest. These include waterfalls, volcanoes, hot springs, rock pillars, fossils and minerals.
Country parks
Country parks are areas protected upon request of local government and mandated by them. The parks are primarily intended for recreational purposes and open to the general public.
Areas protected by special law
Þingvellir National park and world heritage site. Lake Þingvallavatn and the watershed, Lake Mývatn and the river Laxá region, Breiðafjörður and Vatnajökull National Park
Three wetland areas are designated Ramsar Areas: Mývatn-Laxá, Þjórsárver and Grunnafjörður, and three new Ramsar sites are suggested for designation.
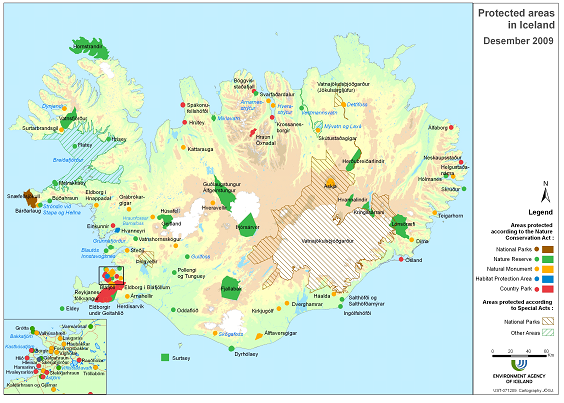
Figure 3. Map of protected areas in Iceland in 2009.
Red list
Redlists are lists of indigenous species that are under threat of extinction in any country or area. The threat is ranked into classes from critically endangered to lower risk.
The Icelandic Institute of Natural History (Náttúrufræðistofnun Íslands) has published two lists for plants and birds. 52 vascular plant species, 67 lichen species, 74 species of moss and 42 marine algae species are on the plant list and about 32 breeding birds are on the birds list (
2)
References
(1) Hrafnsdottir, Th. 2005. Diptera 2 (Chironomidae). The Zoology of Iceland III, 48b: 1-169.
(2) State of the Environment. Report in Icelandic. http://www.umhverfisraduneyti.is/media/PDF_skrar/umhverfiogaudlindir2009.pdf
(3) Gísli Már Gíslason, 2005. Origin of freshwater fauna of the North-Atlantic islands; present distribution in relation to climate and possible micration routes. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 29 (1): 198-203.


Document Actions
Share with others