|
Indicator
|
Indicator past trend
|
Selected objective to be met by 2020
|
Indicative outlook of the EU meeting the selected objective by 2020
|
|
Exposure of terrestrial ecosystems to eutrophication due to air pollution
|
EU

|
EEA

|
Reduce areas of critical load exceedance with
respect to eutrophication by 43 % from 2000 levels
— Air Pollution Thematic Strategy
|

|
|
The area where ecosystems are exposed to eutrophication because of excess atmospheric nitrogen deposition has decreased. According to a scenario assuming that current legislation is fully implemented, it will, nevertheless, fall short of the 2020 objective
|
For further information on the scoreboard methodology please see Box I.1 in the EEA Environmental indicator report 2016
Setting the Scene
The 7th EAP (EU, 2013) includes the objective of reducing the impact of air pollution on ecosystems and biodiversity, with the long-term aim of not exceeding critical loads and levels. Currently, the most important impact of air pollution on ecosystems and biodiversity is eutrophication caused by airborne nitrogen pollution. Excessive atmospheric deposition of nitrogen to ecosystems results in loss of sensitive species, increased growth of species that benefit from high nutrient levels, changes to habitat structure and function, the homogenisation of vegetation types, etc.
Policy targets and progress
The EU Thematic Strategy on Air Pollution includes an objective for 2020, relative to 2000, of a 43 % reduction in areas or ecosystems exposed to eutrophication, i.e. areas where eutrophication critical loads are exceeded (EC, 2005a). The reference measure for this objective is the area in exceedance in 2000 (EC, 2005b). This is in line with the long-term objective of not exceeding critical loads.
In 2000, the area of ecosystems where the critical load was exceeded was about 78 % of the total in the EU Member States (approximately 60 % in all 33 EEA member countries for which data were available, including the 28 EU Member States) and decreased in 2010 to 63 % in the EU (55 % in all 33 EEA member countries). Assuming that current legislation is fully implemented, the area in exceedance is projected to be 54 % in the EU (48 % in all 33 EEA member countries) in 2020 (EEA, 2015). The reduction is approximately 31 % for the EU, as well as for all the 33 EEA member countries, between 2000 and 2020, which is below the 43 % reduction milestone suggested by the air pollution thematic strategy for this period.
Nevertheless, as illustrated in Figure 1, the magnitude (though not the area) of the exceedance is projected to reduce considerably in most areas, except for a few ‘hot spot’ areas, particularly in Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands, as well as in northern Italy. The risk of eutrophication increases slightly when only Natura 2000 protected areas are addressed (EEA, 2014).

Source: CCE (Coordination Centre for Effects), UNECE.
Note: The maps show areas where critical loads for eutrophication of freshwater and terrestrial habitats are exceeded
The main sources of eutrophication are emissions of nitrogen compounds to the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions for the EU decreased by approximately 43 % between 2000 and 2014 (EEA, 2016a). This reduction has been primarily due to the introduction of three-way catalytic converters for cars. However, emission reductions from modern vehicles have not been as large as was originally anticipated. Standard diesel vehicles, for example, can emit up to seven times more NOx in real‑world conditions than in official tests (EEA, 2016b).
NH3 emissions have not fallen by as much. In 2014, they had fallen by approximately 9 % compared with their value in 2000 for the EU. Agriculture dominates emissions of NH3 (AIRS_PO3.2, 2016).1; they amount to approximately 95 % of total emissions in the EEA-33 region. Emissions primarily arise from the decomposition of urea in animal wastes and uric acid in poultry wastes.
A key driver behind the observed reductions was the implementation of the National Emission Ceilings Directive (EU, 2001), which regulates, inter alia, emissions of the eutrophying air pollutants NOx and NH3. However, eutrophying emissions not only from the agriculture and road transport sectors but also from shipping and air travel have been and will remain significant contributors to eutrophication caused by air pollution.
Further reductions in eutrophying air pollutant emissions are expected, inter alia, as a result of the 2012 amended Gothenburg Protocol, which sets air pollutant emission ceilings for 2020 (UNECE, 2012). Nevertheless, as illustrated by the results of the current legislation scenario (Figure 1), the decreases anticipated for 2020 are not expected to contribute sufficiently to reductions in the ecosystem area exposed to excess nitrogen deposition and affected by eutrophication. In 2020, more than 50 % of the ecosystem areas are expected to be at risk of eutrophication in the EU.
The 2020 thematic strategy objective will therefore not be met unless additional measures to mitigate nitrogen emissions are introduced, through further specific and targeted (technical) measures, particularly in the agriculture and transport sectors. Dietary changes resulting in less meat and dairy farming and the reduced use of petrol and diesel in cars could also contribute to reductions.
Country level information
Figure 2 shows the percentage of the area by country where the critical loads for eutrophication were exceeded in 2010 and the areas where exceedance is expected in 2020. Although a decrease is predicted by 2020, if current legislation is implemented, the area showing exceedance will be above 50 % in most countries (see bars). Extremely high magnitudes of exceedance can be found in Denmark, Hungary, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Switzerland, caused by high deposition rates and/or ecosystems that are very sensitive to an excess supply of nitrogen from the atmosphere (see dots), for example nutrient-poor grasslands.
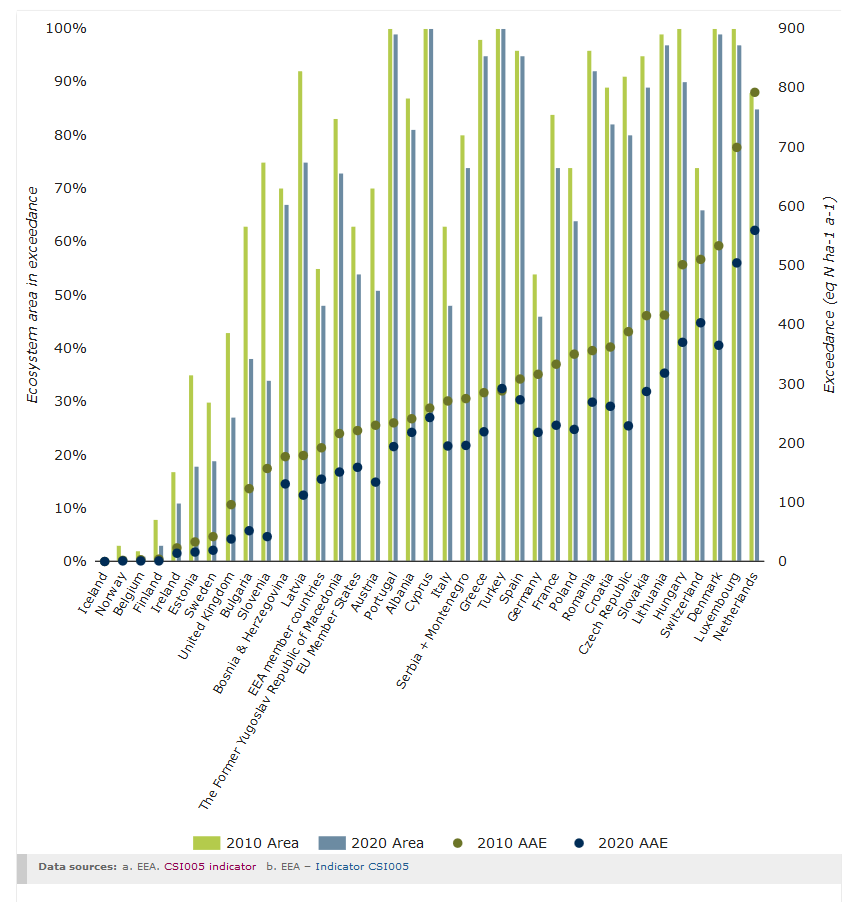
Note: AAE is the average accumulated exceedance, showing the magnitude of exceedance in equivalents (mol nitrogen/ha per year). The data are based on the revised Gothenburg Protocol emission reduction agreements of 2012 (assuming for the 2020 scenario that current legislation is fully implemented). Data for Serbia and Montenegro are presented as aggregated data.
Outlook beyond 2020
The updated air pollution strategy proposed by the European Commission in late 2013 aims to achieve a situation in which the EU ecosystem area exceeding critical loads for eutrophication is reduced by 35% by 2030, relative to 2005 (EC, 2013). This target would not be met if only current legislation was fully implemented. In the EU, the area at risk of eutrophication is projected to decrease only slightly by 2030. The 35 % reduction target would be met in 2030 if the maximum number of technically feasible reduction measures was implemented (EEA, 2015).
As part of the air pollution strategy package, the European Commission has put forward a revised National Emission Ceilings (NEC) Directive. This proposes more ambitious national commitments to reduce emissions, compared with the current Directive (EC, 2001), for the two eutrophying air pollutants, NOx and NH3, among other things. These new ceilings will be applicable from 2020 and 2030 and will contribute to the achievement of the objective of 35% by 2030.
Beyond 2030, a time horizon of 2050 has been proposed as an aspirational year in which to achieve Europe’s long-term objectives, i.e. that air pollution does not lead to unacceptable harm to human health and the environment.
About the indicator
The indicator shows area and quantitative information for ecosystems where atmospheric nutrient nitrogen deposition is above the critical load. A critical load is a “quantitative estimate of an exposure to one or more pollutants, below which significant harmful effects on specified sensitive elements of the environment do not occur according to present knowledge” (UNECE, 2015). Deposition loads of eutrophying airborne pollutants above the critical loads are termed an 'exceedance'.
Exposure in an ecosystem for which information on critical loads is available, is calculated as the average accumulated exceedance (AAE). The AAE is the area-weighted average of exceedances, accumulated over all sensitive habitats (or ecosystem points) defined in a grid cell.
Document Actions
Share with others