
This diagramme shows the range of surface area covered by nationally designated areas in four different and contrasting EEA member countries. Bulgaria has 80% of its protected areas under 100 ha and none over 1000ha whereas Greece has 94% of its protected areas above 100ha and 7% over 10 000 ha. Italy and Poland show the largest range of size of protected area between less than 1 ha and more than 10 000 ha

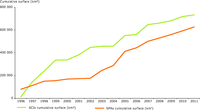
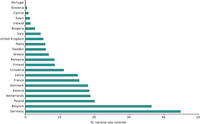
In terms of overall number, Estonia, Norway, Slovakia and Sweden have the most protected areas classified
as Category Ia and Ib, and Category II. Albania, Bulgaria, Estonia and Slovenia have the highest number
of protected areas under Category III, but not all countries classify protected areas under this category.
The United Kingdom is the only country within the 39 EEA member and collaborating countries that has no
protected areas in categories I, II or III. No data available for Ireland.
-
-
-

-
-
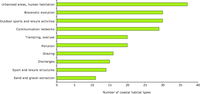
This diagram shows the number of marine species affected by pressures reported by 40% of EU countries where these species occur.
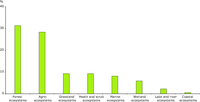
These broad ecosystem‑types represent different ways of clustering CLC units, so there are overlaps between them. For
instance, 'grasslands' and part of 'heaths and scrubs' are included in 'agro-ecosystems'. Similarly, 'lakes and rivers' are
included in 'wetlands'. This is why the sum of the ecosystems is over 100 %.

This diagramme shows the change in area covered by broad ecosystem-types between 2000 and 2009 inside and outside nationally designated areas. The way how “broad ecosystem-types” are defined is described in the EU 2010 Biodiversity Baseline (http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/eu-2010-biodiversity-baseline).

Grid cells indicating where areas at risk of eutrophication in 2010 are reduced by more
(dark orange shading) and less (red shading) than 30 % in comparison to the 1990
situation, when using original (left) and present (right) knowledge.
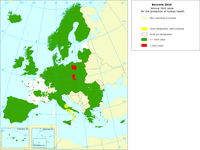
In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set a limit value for benzene (C6H6) for the protection of human health: the annual mean value may not exceed 5 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3). The limit value comes into effect for data measured from 1 January 2010. During 2009 a margin of tolerance was in place so the annual mean should not exceed 6 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3).
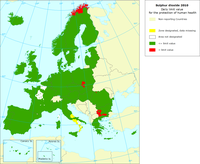
In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50) the EU has set two limit values for sulphur dioxide (SO2) for the protection of human health: the SO2 hourly mean value may not exceed 350 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3) more than 24 times in a year and the SO2 daily mean value may not exceed 125 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3) more than 3 times in a year.
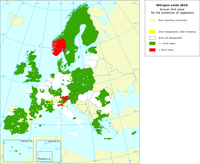
In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set a critical level for nitrogen oxides (NOx) for the protection of vegetation within the zones designated by member states: the NOx annual mean value may not exceed 30 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3).

In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set two limit values for nitrogen dioxide (NO2) for the protection of human health: the NO2 hourly mean value may not exceed 200 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3) more than 18 times in a year and the NO2 annual mean value may not exceed 40 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3). These limit values come into force for concentrations measured from 1.1.2010 so during 2009 a margin of tolerance equal to an annual mean value of 42 micrograms per cubic metre (μg/m3) is still in place

In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set two limit values for sulphur dioxide (SO2) for the protection of vegetation within the zones designated by member states: the SO2 annual mean value may not exceed 20 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3) and the SO2 mean value for the winter period (1 October to 31 March) may not exceed 20 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m3).
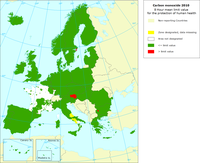
In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set a limit value for carbon monoxide (CO) for the protection of human health: the CO maximum daily 8-hour mean values may not exceed 10 milligrams per cubic metre (mg/m3).
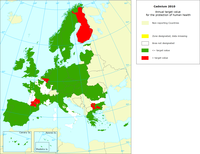
In the directive 2004/107/EC (Fourth Daughter Directive), the EU has set a target value for cadmium (Cd) for the protection of human health: the Cd annual mean value may not exceed 5 nanograms per cubic metre (ng/m3). The target value enters into force 31.12.2012.
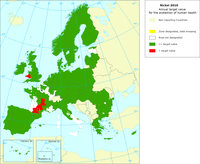
In the directive 2004/107/EC (Fourth Daughter Directive), the EU has set a target value for nickel (Ni) for the protection of human health: the Ni annual mean value may not exceed 20 nanograms per cubic metre (ng/m3). The target value enters into force 31.12.2012.
In the air quality directive (2008/EC/50), the EU has set a limit value for lead (Pb) for the protection of human health: the Pb annual mean value may not exceed 0.5 milligrams per cubic metre (µg/m3) except in the immediate vicinity of specific, notified industrial sources where the Pb annual mean value may not exceed 1.0 milligram per cubic metre (µg/m3)