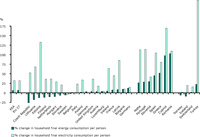
Based on the ratio : energy consumption / population (%/year calculated on the period 1990-2008)
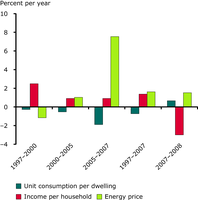
The graph characterizes the average consumption per households (at normal climate) in relation to the evolution of prices and incomes. The income per households for EU-27 as a whole is the sum of the 27 EU countries based on national Odyssee data.
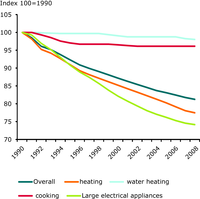
For households, the ODEX is carried out at the level of 3 end-uses (heating, water heating, cooking) and 5 large appliances (refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, dishwashers and TVs)
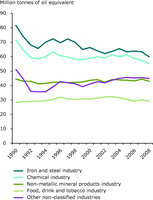
The figure shows the development of the final energy consumption in the different industry sectors.
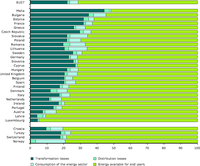
How to read the figure: % Share of 101300 (consumption – energy sector), 101400 (distribution losses), 101500 (energy available for final consumption), Transformation losses (101000 Transformation input minus 101100 Transformation output) within the sum of the above four elements for each Member State

How to read the figures: % share of Gross Inland Energy Consumption (100900) for 2000 Solid Fuels, 3000 Crude oil and Petroleum Products, 4000 Gas, 5100 Nuclear Energy, 6000 Imports/exports electricity, 5500 Renewable Energies, 7100 Industrial Wastes. All in ktoe.
% share of Gross Inland Energy consumption (100900) for Transformation losses (101000 Transformation input minus 101100 Transformation output), 101400 Distribution losses, 101300 consumption – energy sector, 101600 final non-energy consumption, 101800 final energy consumption – industry, 101900 final energy consumption – transport, 102010 final energy consumption – households, 102030 final energy consumption – agriculture (plus 102035 final energy consumption fisheries), 102035 final energy consumption – services, 102040 final energy consumption – other sectors.

The chart shows the estimated contributions of the various factors that have affected emissions from public electricity and heat production (including public thermal power stations, nuclear power stations, hydro power plants and wind plants).
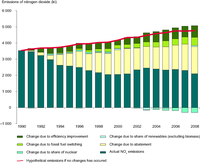
The chart shows the estimated contributions of the various factors that have affected emissions from public electricity and heat production (including public thermal power stations, nuclear power stations, hydro power plants and wind plants).

The chart shows the estimated contributions of the various factors that have affected emissions from public electricity and heat production (including public thermal power stations, nuclear power stations, hydro power plants and wind plants).

Emissions intensity of sulphur dioxide from public conventional thermal power production

CO2, SO2 and NOx emissions and electricity and heat production in the EEA-32, during the period 1990-2008

Emissions intensity is calculated as the amount of pollutant produced (in tonnes) from public electricity and heat production divided by the output of electricity and heat (in toe) from these plants.

Emissions intensity of carbon dioxide from public conventional thermal power production

Emissions intensity of public conventional thermal power production, EEA-32
The European Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (E-PRTR) is a web-based register established by Regulation (EC) No 166/2006 which implements the UNECE PRTR Protocol.

Data from Corine Land Cover (CLC) for the years 1990 and 2006; results aggregated per landscape units of 25 x 25 km2.
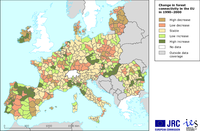
Data from Corine Land Cover (CLC) for the years 1990 and 2000; results aggregated per provinces (Nuts 2/3).
F3v0 - Urban morphological zones (UMZ) are defined by Corine land cover classes considered to contribute to the urban tissue and function
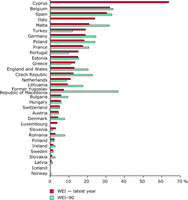
WEI: annual total water abstraction as a percentage of available long-term freshwater resources.
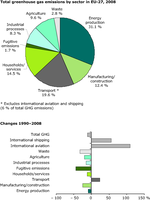
The figures shows the total greenhouse (GHG) emissions in the EU-27 by sector and the changes between 1990 and 2008