
Pollution events are more likely to occur under temperature inversion conditions. During extended periods of high pressure in winter months, solar radiation reaches the ground, warming it up. At night, the lack of cloud cover means the ground loses heat rapidly and the air in contact with the ground becomes colder. The warmer air rises and acts as a lid trapping the colder air close to the ground. Pollution, including that from road traffic is also trapped, so the air layer closest to the ground becomes more and more polluted. This continues until the prevailing meteorological conditions change.

EU progress in meeting emission ceilings (for compliance and for environmental objectives) of the four main air pollutants regulated in the 2001 National Emission Ceilings Directive
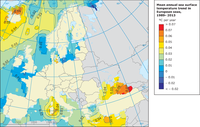
Linear trend in sea surface temperature (in °C/yr) for the European seas over the past 25 years (1989-2013) . Areas where where ice coverage constituted more than 20% are masked.
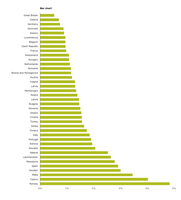
The chart show the average annual percentage change in soil sealing between 2006 and 2009, relative to the sealed area in 2006.
This data set compiles Member State reports on the application of Directive 2003/87/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of the European Union (EU) establishing the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). Article 21 of the Directive stipulates that, each year, Member States should report on the application of the Directive. These reports should be based on the ‘Article 21 questionnaire’, which was adopted by the European Commission in Implementing Decision 2014/166/EU. Article 21 further stipulates that, on the basis of the Member States’ reports, the Commission should publish a report on the application of this Directive.
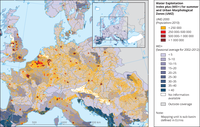
The water exploitation index plus (WEI+) compares water use against renewable water resources. The map illustrates the relation between Urban Morphological Zone and the WEI+ at the sub-basin scale for summer months (July, August and September) defined in calendar year.
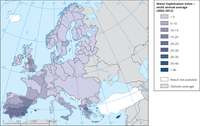
The water exploitation index plus has been calculated as a multi-annual average per river basin district, for the years 2002-2012, as defined in ECRINS. The ECRINS delineation of river basin districts differs from those defined by Member States under the Water Framework Directive, particularly for transboundary river basin districts.
Click on the "downloads and more info" button below to see the dynamic map with time slider, which provides information on water abstraction by source and water use by sector at sub-basin or river basin scale.

The figure shows the background concentrations of PM10 observed at traffic stations in 2013. The two highest PM10 concentration classes (dark orange and light orange) correspond to the 2005 annual limit value (40 μg/m3) and to a statistically derived level (31 μg/m3) corresponding to the 2005 daily limit value. The lowest class corresponds to the WHO air quality guideline for PM10 of 20 μg/m3.
