Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 17 Feb 2025
The unique
geographical features of Hungary
– the Carpathian Basin surrounded by mountains – its
climate, its hydrological characteristics and topographic and lithologic
diversity allowed the evolution of diverse landscapes and an extremely rich flora
and fauna.
The country – located in the middle
of the Carpathian
Basin - constitutes a
specific ecological unit, making up a substantial part of the Pannonian
biogeographical region, one out of the nine biogeographical regions of the
European Union. The region is connected, inter alia, to the flora of the
Carpathians, the Eastern Alps and the West
Balkans (See map 1). This poses a challenge and puts major
responsibility on Hungary*
to maintain these natural assets and facilitate the continued connection with
the surrounding biogeographical regions.
Natural
habitats, as well as genetic resources of the wild flora and fauna in the
country, show a high level of diversity. Around 2 800 different vascular
plant species (2 300 native), and 43 000 animal species in Hungary
have been observed. Owing to the long-lasting geographical isolation of the Carpathian Basin, there is also a high abundance of
endemic species. Their proportion is extremely high (10-30 %) within some invertebrate
groups, and as regards plants, 2 % of the Hungarian flora can be found
exclusively in the Carpathian
Basin.
Biodiversity – including
agrobiodiversity and cultural landscapes – is an exceptional opportunity for sustainable
social and economic development. At the same time, special attention should be
paid to the expectedly significant regional impacts of climate change, leading
to a higher vulnerability of the natural flora and fauna and the ecosystem
services.
Map
1. Biogeographical Regions in Europe
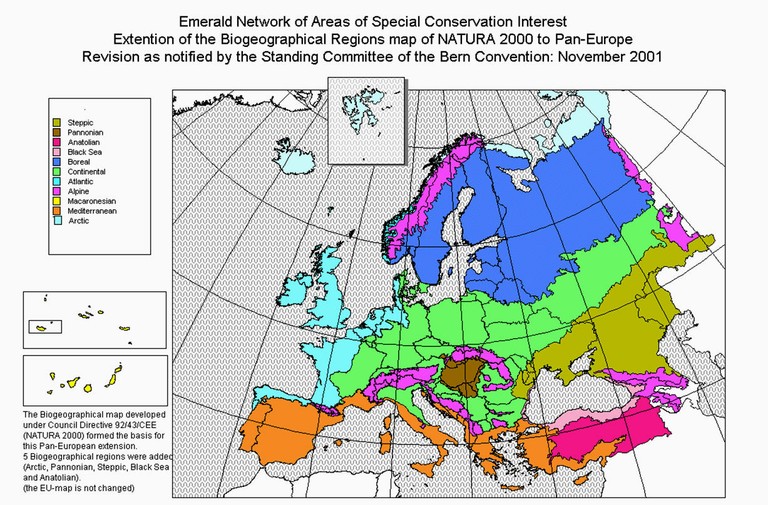
Source: UNEP/GRID
*in cooperation with the Czech
Republic, Slovakia,
Romania,
having a smaller proportion of the Pannon biogeographical region

Document Actions
Share with others