All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesArable land and permanent crops gains and losses between 2000 and 2018
Map (static)
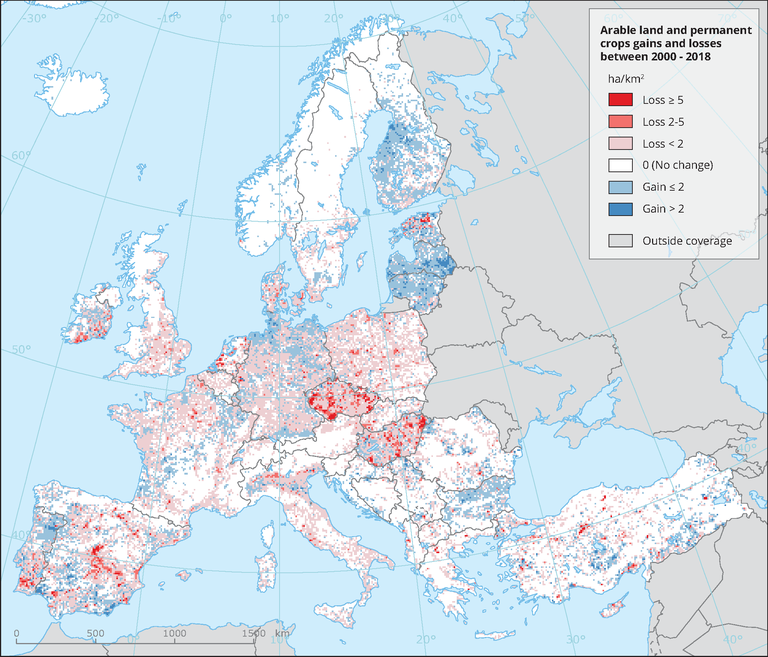
This map shows the loss and gain of arable land and permanent crops. Changes are monitored at 1 ha level whereas the map is aggregated in a 10 km2 grid.
- Albania
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kosovo
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- North Macedonia
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
Methodology
The following CLC classes were used to process the map:
CLC_CODE LABEL1 LABEL2 LABEL3
- 211 Agricultural areas Arable land Non-irrigated arable land
- 212 Agricultural areas Arable land Permanently irrigated land
- 213 Agricultural areas Arable land Rice fields
- 221 Agricultural areas Permanent crops Vineyards
- 222 Agricultural areas Permanent crops Fruit trees and berry plantations
- 223 Agricultural areas Permanent crops Olive groves
- 241 Agricultural areas Heterogeneous agricultural areas Annual crops associated with permanent crops
Additional information
Sectoral trends and high societal demand for agriculture and forestry outputs lead to pressures on land and soil. This has a range of negative environmental impacts, such as loss of biodiversity, , eutrophication, pressures on freshwater ecosystems or air pollution. Loss of arable land due to, for example, land abandonment in many cases causes loss of habitats for farmland species (Chapter 3). At the same time droughts, forest fires and floods are increasing threats, in particular in southern Europe. Sustainable management of our land and soil resources helps to maintain agricultural and forest productivity while improving the potential of land and soils as a carbon sink, supporting biodiversity and storing and filtering water and nutrients.
