Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
Montenegro is located in south-eastern Europe on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. Its geographical coordinates are 4° 30' N, 19°18' E. The total area of the country is 13,812 km2 of which 13,452 km2 is land and 360 km2 water. Land boundaries bordering five countries total 625 km and the coastline 300 km. Montenegro has a Mediterranean climate with hot dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy snowfalls inland. The terrain is a highly indented coastline with a narrow coastal plain backed by rugged high limestone mountains and plateau. The elevation varies between 0 m on the coast to a highest point of 2 522 m above sea level at Bobotov Kuk. Agricultural land covers 5 165 km2 of the country, 37.4 %, arable land 13.7 % and permanent crops 1 %. Agricultural crops grown are cereals, potatoes, tobacco, grapes, citrus fruit, olives and figs. The main natural hazard in Montenegro is destructive earthquakes.
Figure 1. Map of Montenegro
Source: EPA – Montenegro
Population Density
According to the 2003 census, Montenegro had a declining population of 620 145 inhabitants with an average density of 44.9 per km². At the time of the last census Montenegro was a civic state and the new constitution, adopted in 2007, recognises the main ethnic groups: Montenegrins 44.5 %, Serbs 33.6 %, and Bosnian-Muslims 12.7 %, Albanians 5 %, others: 4.2 %. This summed to 99.9%. It has been adjusted to 100%
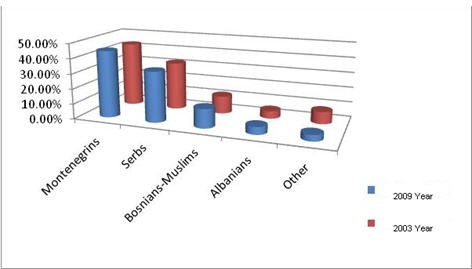
Figure 2. Ethnic groupings in Montenegro
Source: Statistical office of Montenegro (Monstat)
Economic structure
Montenegro has benefitted from EU autonomous trade measures since 2000. In 2007, both exports and imports of goods and services increased, representing respectively 57 % and 104.7 % of GDP. The main sources of export revenues are tourism and aluminium production. The EU is the main trading partner of the country, also with reference to foreign direct investments, which in 2007 represent 44.2 % of GDP, with the EU-27 accounting for half of total inflows. Since January 2008, access of Montenegrin products to the EU has been expanded and EU exports to Montenegro have been granted trade preferences following the enforcement of the Interim Agreement.
Since 2002, the currency in Montenegro has been the Euro. Total GDP in 2007 was €2 807.9 million and GDP per person €4 484. Growth of GDP, at constant prices, was 10.7 % in 2007.
The rate of poverty in Montenegro has fallen significantly: the percentage of poor people decreased from 11.3 % in 2006 to 8.0 % in 2007, the consequence of overall economic growth, and growth of income and expenditure of households.
Transformation from communist to democratic system
The Republic of Montenegro became an independent state following the referendum on 21 May 2006. Before gaining independence, Montenegro was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, from 27 April 1992 until February 2003. One year later, Montenegro became part of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro (SCG).
Montenegro has undergone two transitions in the past decade, the first introduced a multiparty system – the so-called ‘anti-bureaucratic’ revolution of 1989 – the second started in 1996 and ended with the fall of Milosevic on 5 October 2000 when the process of economic and political consolidation, which was completed in the referendum in 2006, started.
In the 2007 constitution, Montenegro is defined as a civil, democratic, ecological and social justice state.
Government
The government of Montenegro has 17 ministries, with the Ministry of Spatial Planning and Environment responsible for creating policy and legislation. The Agency for Environmental Protection was established on 16 November 2008 and is responsible for the implementation of environmental legislation.
The Ministry of Spatial Planning and Environment is responsible for the institutions that are active in the field of environmental protection: the Agency for Environmental Protection, the Hydro-meteorological Service, the Public Institution Centre for Eco-toxicological testing, the Institute for Nature Protection, the Public Enterprise for National Parks of Montenegro, the Public Enterprise for Coast Regional Water Supply, the limited liability company ‘Procon’, and the Public Enterprise for managing marine property.


Document Actions
Share with others