
Data viewer on greenhouse gas emissions and removals, sent by countries to UNFCCC and the EU Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Mechanism (EU Member States).
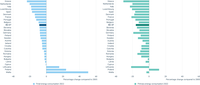
This chart shows the change in energy consumption of EU Member States in 2022 compared to 2005.

The map shows the share of woody landscape features in agricultural areas on NUTS3 regions.

Historical and projected GHG emissions reported by the EU Member States and quality checked by the EEA. Values expressed in MtCO₂e. For historic years, disaggregation to 4 subcategories is available. There are two scenarios of projected emissions: WEM, with existing measures scenario and WAM, with additional measures scenario.
Access the information on the air pollution Policies and Measures reported by Member States.
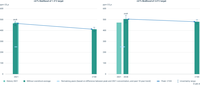
The periods within which peak concentrations could be exceeded are shown by light blue arrows, based on the trend of the past 10 years in total greenhouse gas concentrations and without allowing for a temperature overshoot (based on IPCC, 2019).
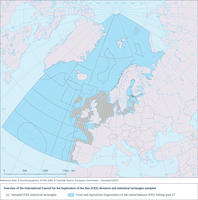
The map shows the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) rectangles covered by the Database Trawl Surveys (DATRAS) surveys over the period analysed (1967-2022).

The charts show:
Top figures: the temporal development in the number of species of each biogeographical affinity group (Atlantic, Boreal, Lusitania and Unknown) by marine region (Greater North Sea, Baltic Sea, Celtic Seas and Bay of Biscay and the Iberian Coast).
Bottom figures: the temporal development of the ratio between Lusitanian and Boreal species and sea surface temperature by marine region to investigate correlations.

The maps show the temporal development of the ratio between the number of warm-favouring (Lusitanian) fish species and the number of cool-favouring (Boreal) fish species by The International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) statistical area in 8-year intervals from 1982 to 2022.
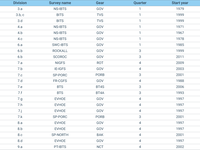
The table shows the Survey name, the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) sub-division in which the survey is undertaken, the gear used in the survey, the initial start date of the survey and the quarter used for the assessments.