Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
A reduction in the leaching and run-off of nutrients from the agricultural sector and an improved sewage treatment has led to a significant improvement of the Danish aquatic environment.
Livestock production produces approximately 35 million tonnes of liquid and solid manure per year. This is used in agricultural crop production in addition to commercial fertilisers. Excess nitrogen leaching to the aquatic environment was reduced by 12 % from 2000 to 2007. Excess nitrogen leaching data in 2008 is not available, however surplus nitrogen continues to decrease and from 2007 to 2008 by 1 %. The surplus phosphorus decreased by nearly 32 % from 2000 to 2008, although a decrease in leaching of phosphorus has not yet been measured.
The pesticide application frequency in agricultural production increased by more than 50 % from 2000 (2.07 times per year) to 2008 (3.16 times per year).
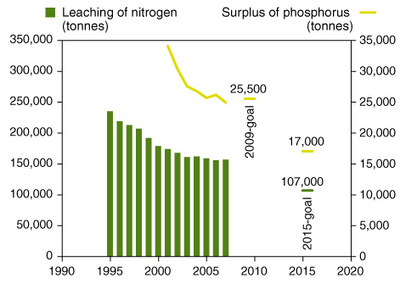
Figure 8 (MTR2009:1.2.1): Leaching of nitrogen from the root zone and surplus phosphorus in the agricultural sector. The Danish ’Green Growth‘ plan set new reduction targets for nitrogen and phosphorus. For phosphorus, the target is defined differently compared to the previous set reduction target (i.e. Water Environment Plan III) and therefore cannot be compared with existing data. Therefore the old target is shown in the figure. The target for nitrogen set in the ’Green Growth‘ plan is recalculated to a figure for leaching from the root zone as shown in the figure. Source: Faculty of Agricultural Sciences and National Environmental Research Institute.
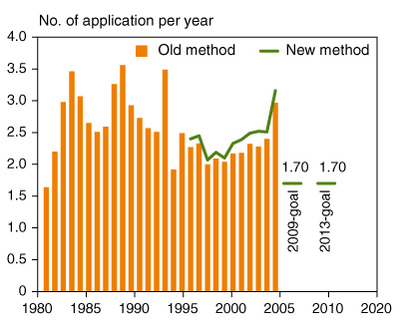
Figure 9 (1.2.2): Frequency of pesticide application in Danish agriculture. Because the calculation method changed in 1998 and the target set for frequency of application is based on an old method, both are shown. Reference: Statistics Denmark and The Danish Environment Agency.
The main part of the use of freshwater in Denmark is from groundwater resources, including industrial and agricultural use. Exploitation of groundwater has decreased since the beginning of the 1990s and has been stable since 2000. Consumption through the public water supply accounted for 60 %, agriculture and aquaculture for 34 % and industry for 6 % in 2006.
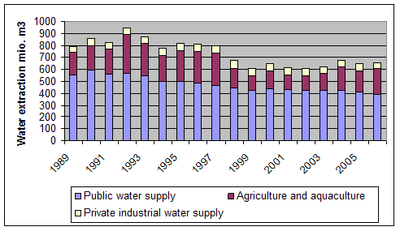
Figure 10 (3.4.1): Water extraction in Denmark including public water supply, commercial water supply (agriculture and aquaculture) and industrial production. Figures from 2007-2008 is not included due to the implementation of a new municipality reform in Denmark. Source: Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS).
Document Actions
Share with others