Published: 30 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
The increase in population
and considerable migration of the population towards the developed cities in Albania
have resulted in increased consumer behaviour and, therefore, increased volumes
of municipal waste. The huge
transformation of the economy of the country has been accompanied by changes and an increase
in the consumption of consumer goods by the population: this is shown directly by
the increase in the level of packaging waste of different products.
In 2005, the
amount of municipal waste per inhabitant was at a lower level compared to 2009,
when, as is seen in Figure 3, the amount clearly increased.
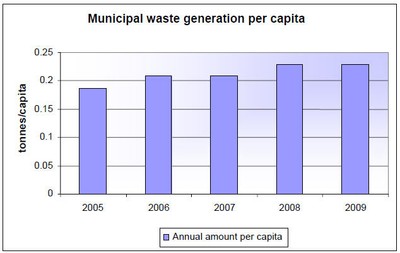
Figure 3:
Municipal waste generated 2005–09
Source:
Ministry of Public Works, Transport and Telecommunication
Daily production of municipal waste
per inhabitant is approximately:
- urban areas (50 % total
population): 0.8 kg/day
- rural areas (50 % of total
population): 0.35 kg/day
Weak waste
management leading to dumping of waste without any separation and treatment in landfill
sites causes pollution emissions to air and water.
Polluted
waters created at landfill sites present a high risk of pollution to surface
waters and groundwater and biodegradable waste through its decomposition releases
methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gases to the atmosphere.
Municipal waste in Albania
contains a high percentage of organic waste and no recycling methods exist to
reduce the amount of organic waste disposed of in landfills. The organic waste
in landfills is the main source of CH4 emissions. Methane emissions
during the period 1990–2000 are presented in Figure 4.
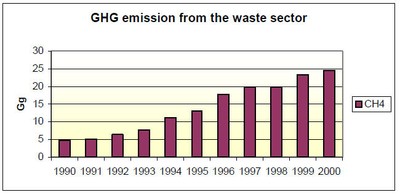
Figure 4: Methane emissions 1990–2000
Source: Climate Change Program, UNDP
The most effective abatement
measure would be the introduction of landfill gas recovery plants that would recover
70 % of the methane; however, this measure is still not implemented.
Promoting sustainable waste
management practices can also reduce GHG emissions. The main goals of
integrated waste management are to:
- reduce solid waste,
- pursue recycling and reuse of material,
- regulate the disposal of solid
waste.
Recycling and composting should be the top priority
measures to reduce GHG emissions in Albania.


Document Actions
Share with others