All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesClimate change has increased forest fire risk across Europe. Even so, the burnt area of the Mediterranean region has decreased slightly since 1980, indicating that fire control efforts have been effective. However, in recent years, forest fires coinciding with record droughts and heatwaves have affected regions in central and northern Europe not typically prone to fires. An expansion of fire-prone areas and longer fire seasons are projected in most European regions, in particular for high emissions scenarios, so additional adaptation measures are needed.
Figure 1. Burnt area in European countries (based on EFFIS data)
| Years | Portugal | Spain | France | Italy | Greece | Total EUMED5 | Other countries (outside EUMED5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 44.251 | 263.017 | 22.176 | 143.919 | 32.965 | 506.328 | |
| 1981 | 89.798 | 298.288 | 27.711 | 229.85 | 81.417 | 727.064 | |
| 1982 | 39.556 | 152.903 | 55.145 | 130.456 | 27.372 | 405.432 | |
| 1983 | 47.811 | 108.1 | 53.729 | 212.678 | 19.613 | 441.931 | |
| 1984 | 52.71 | 165.119 | 27.202 | 75.272 | 33.655 | 353.958 | |
| 1985 | 146.254 | 484.476 | 57.368 | 190.64 | 105.45 | 984.188 | |
| 1986 | 89.522 | 264.887 | 51.86 | 86.42 | 24.514 | 517.203 | |
| 1987 | 76.269 | 146.662 | 14.108 | 120.697 | 46.315 | 404.051 | |
| 1988 | 22.434 | 137.734 | 6.701 | 186.405 | 110.501 | 463.775 | |
| 1989 | 126.237 | 426.693 | 75.566 | 95.161 | 42.363 | 766.02 | |
| 1990 | 137.252 | 203.032 | 72.625 | 195.319 | 38.594 | 646.822 | |
| 1991 | 182.486 | 260.318 | 10.13 | 99.86 | 13.046 | 565.84 | |
| 1992 | 57.011 | 105.277 | 16.593 | 105.692 | 71.41 | 355.983 | 87.244 |
| 1993 | 49.963 | 89.267 | 16.698 | 203.749 | 54.049 | 413.726 | 64.984 |
| 1994 | 77.323 | 437.635 | 24.995 | 136.334 | 57.908 | 734.195 | 76.057 |
| 1995 | 169.612 | 143.484 | 18.137 | 48.884 | 27.202 | 407.319 | 20.877 |
| 1996 | 88.867 | 59.814 | 11.4 | 57.988 | 25.31 | 243.379 | 47.368 |
| 1997 | 30.535 | 98.503 | 21.581 | 111.23 | 52.373 | 314.222 | 29.458 |
| 1998 | 158.369 | 133.643 | 19.282 | 155.553 | 92.901 | 559.748 | 52.916 |
| 1999 | 70.613 | 82.217 | 15.906 | 71.117 | 8.289 | 248.142 | 35.674 |
| 2000 | 159.605 | 188.586 | 24.078 | 114.648 | 145.033 | 631.95 | 178.422 |
| 2001 | 111.85 | 93.297 | 20.642 | 76.427 | 18.221 | 320.437 | 56.394 |
| 2002 | 124.411 | 107.464 | 30.16 | 40.791 | 6.013 | 308.839 | 42.435 |
| 2003 | 425.726 | 148.172 | 73.278 | 91.805 | 3.517 | 742.498 | 78.134 |
| 2004 | 129.539 | 134.193 | 13.711 | 60.176 | 10.267 | 347.886 | 19.193 |
| 2005 | 338.262 | 188.697 | 22.135 | 47.575 | 6.437 | 603.106 | 22.612 |
| 2006 | 75.51 | 155.345 | 7.844 | 39.946 | 12.661 | 291.306 | 45.551 |
| 2007 | 31.45 | 86.122 | 8.57 | 227.729 | 225.734 | 579.605 | 93.534 |
| 2008 | 17.244 | 50.322 | 6.001 | 66.329 | 29.152 | 169.048 | 63.362 |
| 2009 | 87.416 | 120.094 | 17 | 73.355 | 35.342 | 333.207 | 28.265 |
| 2010 | 133.09 | 54.77 | 10.3 | 46.537 | 8.967 | 253.664 | 19.258 |
| 2011 | 73.813 | 102.161 | 9.4 | 72.004 | 29.144 | 286.522 | 44.206 |
| 2012 | 110.231 | 226.125 | 8.6 | 130.814 | 59.924 | 535.694 | 84.409 |
| 2013 | 152.756 | 58.985 | 3.608 | 29.076 | 46.676 | 291.101 | 26.372 |
| 2014 | 19.929 | 46.721 | 7.493 | 36.125 | 25.846 | 136.114 | 30.419 |
| 2015 | 64.443 | 103.2 | 11.16 | 41.511 | 7.096 | 227.41 | 32.649 |
| 2016 | 161.522 | 65.817 | 16.093 | 47.926 | 26.54 | 317.898 | 34.602 |
| 2017 | 540.63 | 178.234 | 26.378 | 137.103 | 13.393 | 895.738 | 78.399 |
| 2018 | 44.578 | 25.162 | 5.124 | 19.481 | 15.464 | 109.809 | 50.309 |
| 2019 | 42.084 | 83.963 | 23.477 | 36.034 | 9.153 | 194.711 | 42.502 |
| 2020 | 67.17 | 65.923 | 17.077 | 55.656 | 9.3 | 215.126 | 72.873 |
Forest fires are essential for many ecosystems, for instance for forest renewal, to help control insect and disease damage, and to reduce build-up of fuel and thus future fire intensity. However, frequent and large-scale fires have negative impacts on air and water quality, biodiversity, soil and landscape aesthetics. Forest fires also threaten climate change mitigation, as they release large amounts of greenhouse gases, and they can cause economic damages and loss of human lives in populated areas.
Fire risk depends on many factors including climatic conditions. Climate change is expected to have a strong impact on forest fire risk in Europe, as recognised by the EU strategy on adaptation to climate change. To monitor trends in forest fires, the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS), managed by the Joint Research Centre (JRC), reports on the number of fires and the burnt area, with data on the latter being considered more robust and policy relevant.
Long time series, starting in 1980, are available for Mediterranean Europe — southern France, Greece, Italy, Portugal and Spain (EUMED5). The burnt EUMED5 area has slightly decreased since 1980, with the exception of Portugal . However, there is large interannual variability, determined strongly by meteorological conditions. For example, the burnt area in 2017 was the second largest on record, due in particular to unprecedented fires in Portugal, whereas the burnt area in 2018 was the lowest on record.
For other European countries, data are available from 1992. More countries suffered large forest fires in 2018 than ever recorded before, including in central and northern Europe, regions not typically affected by fires in the past. For instance, Sweden experienced its worst fire seasons ever in 2018 and required international fire-fighting assistance.
Many of the recent extreme fire episodes and devastating fire seasons in Europe were driven by severe weather conditions, with record droughts and heatwaves occurring in the spring and summer of 2017 and 2018 for instance. The new EU climate adaptation strategy aims to build a climate-resilient Europe by mitigating the negative consequences of climate change, such as the impacts of forest fires, by 2050.
Figure 2. Overall weather-driven forest fire danger in the present, and under two climate change scenarios
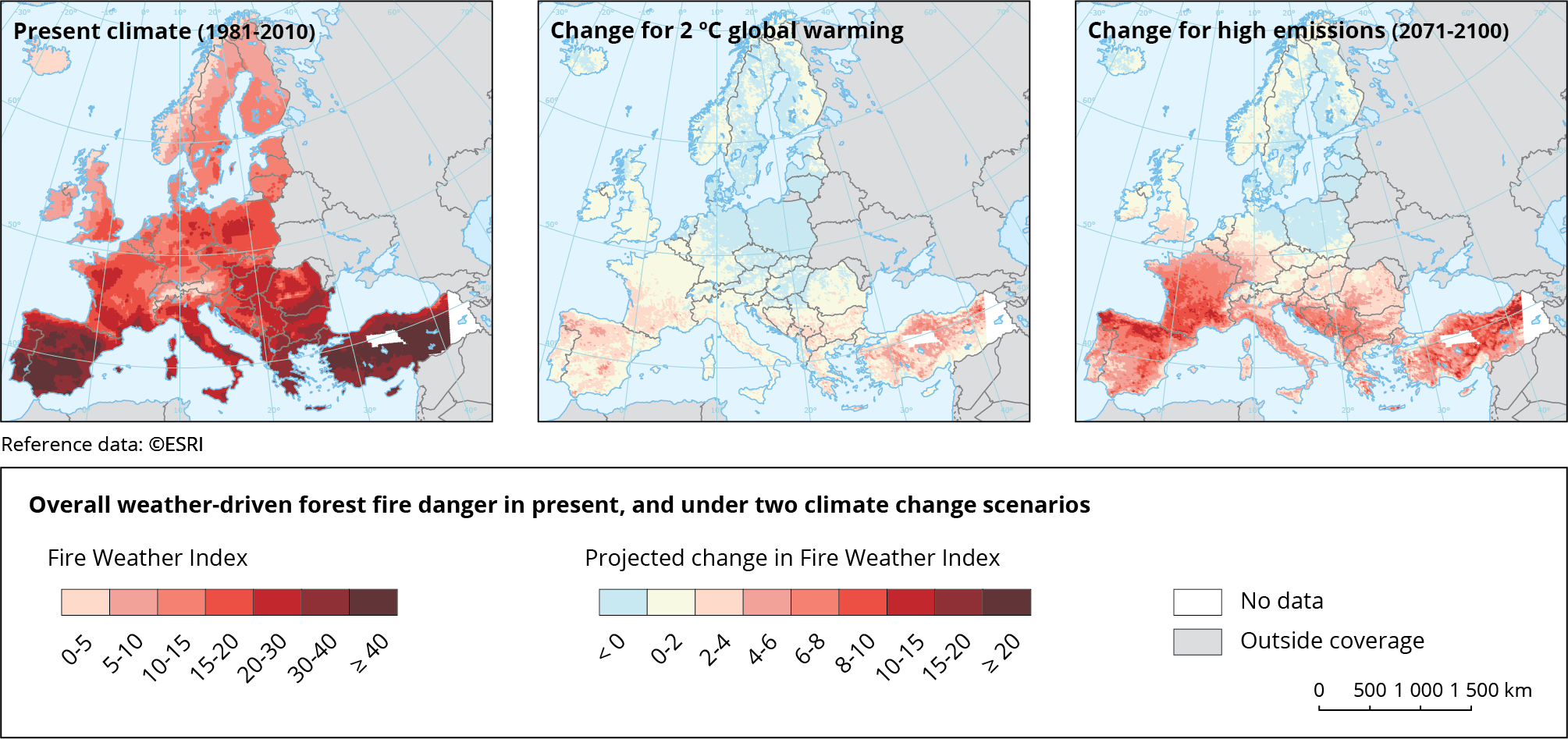
The Canadian Fire Weather Index (FWI) is used to assess fire risk based on meteorological conditions. From 1980 to 2012, the FWI increased for Europe as a whole, particularly in southern and eastern Europe. The fact that the burnt area of the Mediterranean decreased over the same period suggests that fire management and suppression efforts in this region had some effect.
Meteorological fire danger is projected to increase further in most regions, except in parts of north-eastern and northern Europe. This increase is expected to lead to a northward expansion of moderate fire danger zones in western-central Europe, but the countries with the highest absolute fire danger will remain Portugal, Spain and Turkey . Modelling studies indicate that burnt area in EUMED5 countries could double under 3 °C global warming, but that adopting additional measures, such as prescribed burning, fire breaks and enhanced fire suppression could substantially limit this increase .
Further information on past and projected changes in fire weather conditions in Europe is available on the page Wet and dry — fire weather of the recent EEA web report Europe's changing climate hazards. Further information on the health effects of wildfires is available on a dedicated thematic page in the European Climate and Health Observatory.
