Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
Key drivers
Road traffic is the main source of local air pollution in urban areas in Iceland. Consequently NOx and PM are the main pollutants in urban areas.
Key Pressures
Use of studded tyres has been widespread and, for example, in the year 2001, 55 % of particulate matter in Reykjavík on polluted days was due to the wear of asphalt (1).
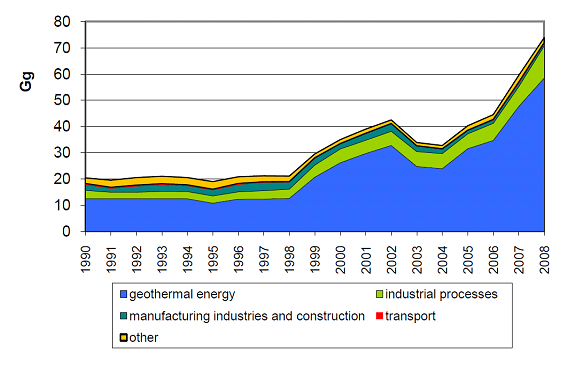
Figure 1. Temporal trend in emissions of SO2 (in Gg) by sector 1990-2008. Emission from geothermal energy is on the form of H2S but is calculated as SO2. (2)

Figure 2. Temporal trend in emissions of NOx ( in Gg) by sector 1990‑2008 (2).
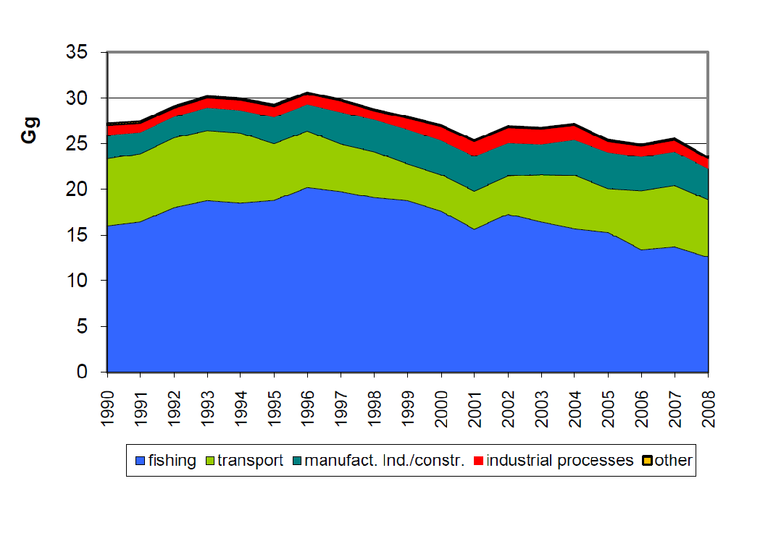
Figure 3. Temporal trend in emissions of NMVOC (non-methane volatile organic compounds(in Gg) by sector 1990-2008 (2).
References
(1) Method for determining the composition of airborn particle pollution. Composition of particle air pollution in Reykjavik. Report in English. http://english.ust.is/media/skyrslur2003/uppruni_svifryks_eng.pdf
(2) Emissions of greenhouse gases in Iceland from 1990 to 2008. National Inventory Report 2010. Report in English. http://www.ust.is/media/fraedsluefni/ICELAND_NIR_2010.pdf



Document Actions
Share with others