Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
Last year for identifying the hot
points and defining the pressures by the catchment protection action plans,
priorities were established including the 25 river catchments of Turkey.
In this study the measured results for 2006, provided by General Directorate of
State Hydraulic Works, were used and with the assistance of those data the
water quality map of Turkey was prepared as below Figure 1.
Figure 1: Water
Quality of Turkey, 2006
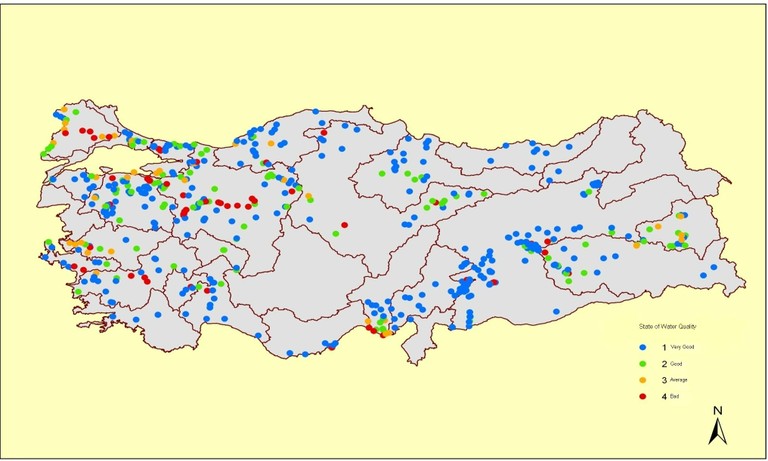
Source: General Directorate of Environmental
Management
The measured results
of heavy metal concentrations in water belonging to 2006 are lower than the
measurement results of organic concentration amount in water for the same year.
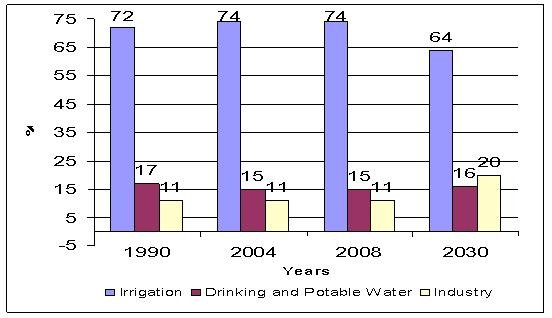
In various sectors, as 34 billion m3
in irrigation, 7 billion m3 in domestic water supply and 5 billion m3
in industry totally 46 billion m3 of water was consumed in 2008.
This sum corresponds to only 41% of the available exploitable potential of 112
billion m3. According to future projections, the share of irrigation
use will decrease from 74% in 2008 to 64% by 2030. On the other hand, the
domestic and industrial use would increase to 16% and 20% in this period, respectively
( Figure 2).
Figure 2: Water Amount Abstracted by
Sectors (milion m3)
Source:
General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works
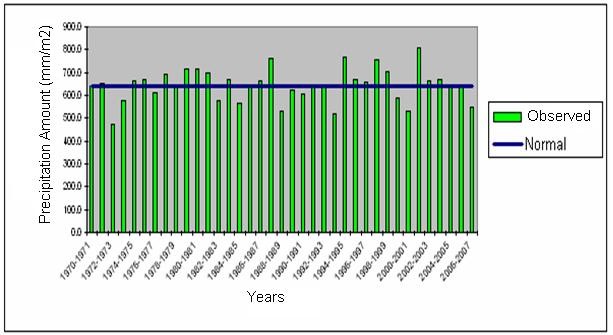
During 2007, drought conditions had a sequence
of fifth dry period of the last 37 years. Yearly total precipitation of Turkey
is 642 mm
per m2, normally. But in 2007 this value decreased to 548 mm. and precipitation
was 15% less than the normal. It’s shown
“Precipitation of Turkey between 1970 – 2007 as water year totals” in Figure 3.
Figure 3:
Precipitation of Turkey
between 1970 – 2007 as water year totals
Source: General Directorate of State
Hydraulic Works
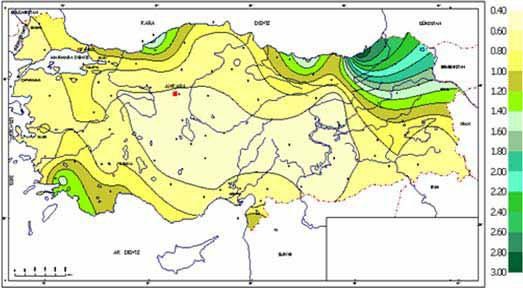
Figure 4: Aridity
assessment of Turkey
based on P/PET relation
Source: General Directorate of State
Hydraulic Works
Flood is the second biggest hazard
in Turkey, which causes huge economic loss after earthquake. According to the
records based on annual flood inventory studies, economic loss related to the
flood disasters reaches 100 million US$/year and in the last 15 years, about 500,000 ha urban and
agricultural areas were affected by floods.
The June-July-August months are the
most popular season for tourists, as well it is the dryest season. In that
period which 42% of the tourists come to Turkey, water use per person increase
by 3-4 times.
In
the city centers that could get water by 80% of population, 13% of the samples
were not up to the standards while in the city centers that could get water by
60% of population, only 5% of the samples were not up to the standards. The number
of municipalities that served with drinking and using water network are tend to
increase in recent years. The municipality number and the rate of the
population served with networks by total population for 2001 and 2006 years are
3092-95% and 3167-98%, respectively.
Document Actions
Share with others