- about 1 096 800 km2 are protected under Natura 2000 and national designation, which represents 25 % of the EU-27 terrestrial land
- Natura 2000 overlaps with nationally designated areas on 7.7 % of the EU land territory
- Natura 2000 covers 9.7 % of the EU land territory beyond existing nationally designated areas
- 7.7 % of the EU land territory is only covered by nationally designated areas
Which means that Natura 2000 contributes to 70% of the total surface area of protected areas within the EU-27.
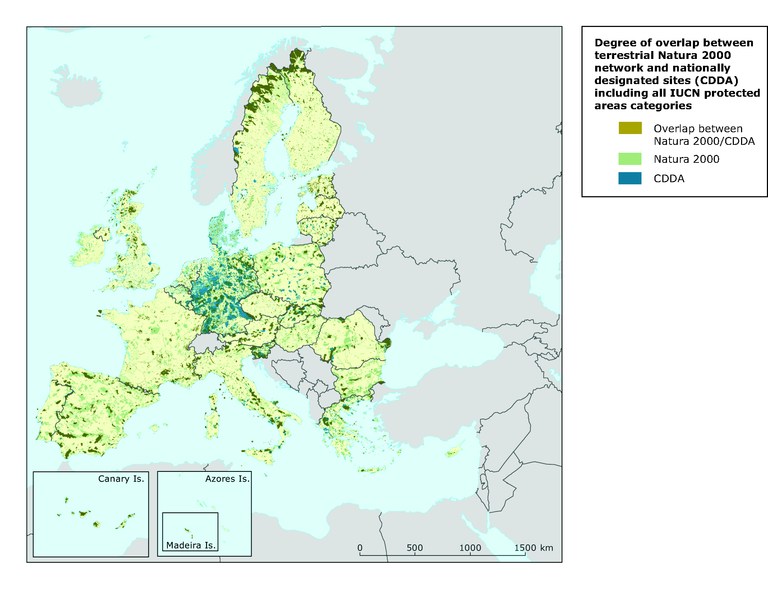
Degree of overlap between terrestrial Natura 2000 network and nationally designated sites
The overlap of Natura 2000 boundaries with the boundaries of nationally designated sites (CDDA) shows very different patterns across the EU (map below). However, it should be stressed that while the Natura 2000 digital maps fully reflect the actual extension of the network, the CDDA digital maps only reflects what countries have reported on a voluntary basis to the European Environment Agency.
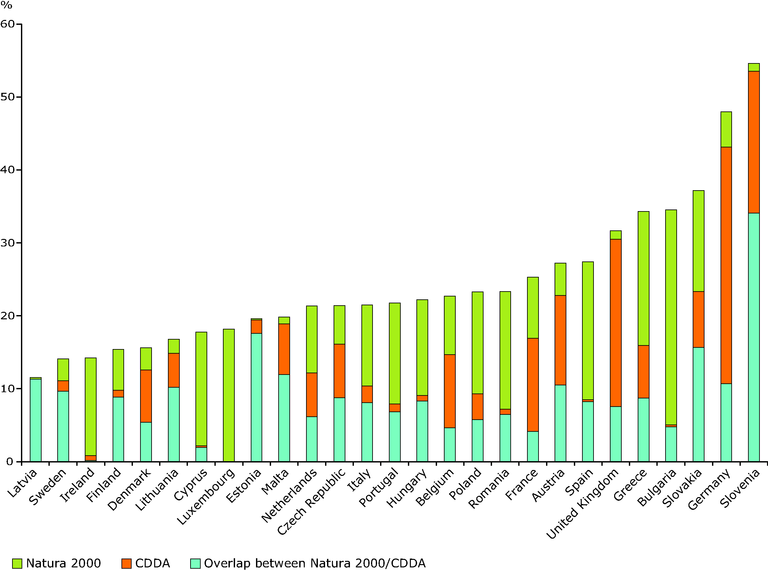
Share of terrestrial area designated in EU Member States under Natura 2000 and national designations
There are some countries (such as Austria, Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Slovenia, and the United Kingdom) where Natura 2000 nearly always overlaps with national designations (CDDA). These countries have few if any Natura 2000 sites that do not overlap with national designations. But the situation is quite different in Bulgaria, France, Greece, Hungary, Italy, and Portugal, where many Natura 2000 sites do not overlap with existing nationally designated sites.
It is also remarkable to notice how, in some countries (Austria, Belgium, Estonia, France, Germany, Slovenia and the United Kingdom), national designations significantly complement the Natura 2000 network in terms of area covered. Although a large part of these national designations are targeted at landscape protection or sustainable territorial development (IUCN management categories V and VI) and not specifically focused on biodiversity conservation, the main goal of Natura 2000 sites.
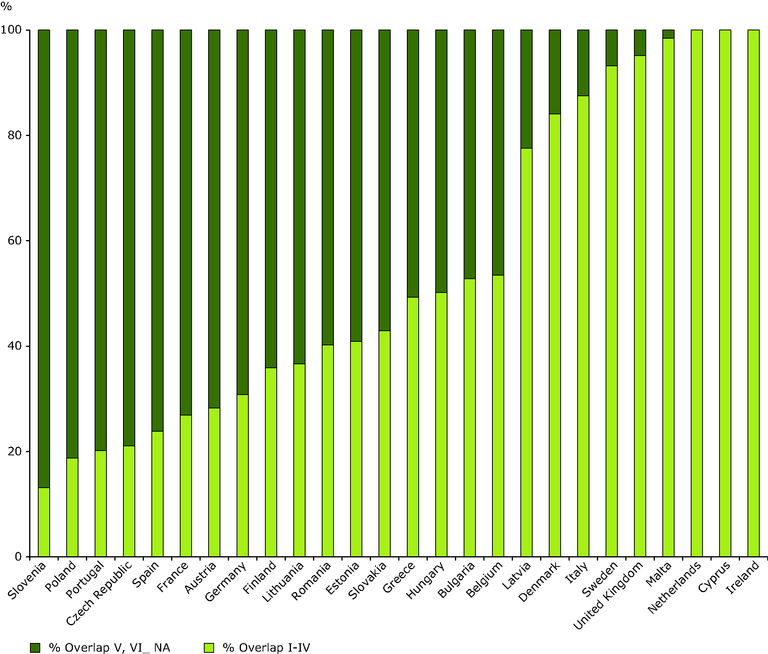
Share of terrestrial area designated at national level under various IUCN management categories overlapping with Natura 2000
The share of spatial overlap between, on the one hand, Natura 2000 and nationally designated sites under IUCN management categories I to IV, and on the other hand, Natura 2000 and nationally designated areas under IUCN management categories V to VI is shown below. The purpose of the Natura 2000 network is primarily to ensure the conservation of targeted species and habitats of European interest. A reasonable supposition might therefore be that, in general, Natura 2000 sites would mostly overlap with nationally designated sites under IUCN categories I to IV (the categories that aim at protecting ecological processes and biodiversity). However, the Natura 2000 network, especially through the Habitats Directive, also provides the opportunity for sustainable development approaches within protected sites in full partnership with local communities and other stakeholders. This type of sustainable development corresponds more closely to the IUCN categories V and VI. It is thus interesting to see to what extent a significant area of Natura 2000 sites is underpinned by nationally designated areas under IUCN categories V and VI across EU Member States.
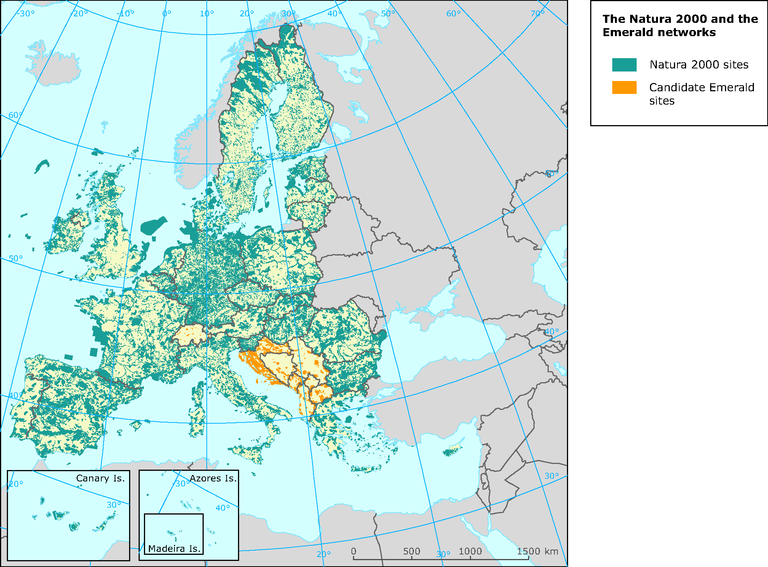
The international networks of Natura 2000 and the Emerald
The Emerald Network and Natura 2000 are based on the same principles, and are thus fully compatible with each other, helping to develop a coherent approach to the protection of natural habitats in the European continent. The map below details the extent of Emerald and Natura 2000 sites.
Document Actions
Share with others