Published: 26 Nov 2010
Modified: 11 May 2020
National
emission ceilings for 2010 within reach
Emissions of air
pollutants will decline towards 2010 with current policies (Figure 7). After
2010, emissions of NOx will continue to decline, but emissions of
other air pollutants will stabilise or will increase again with current
policies. NEC ceilings are projected to be met for SO2 and NMVOC in
2010. For NH3 and NOx, the 2010 emissions will be close to
the national ceiling, so it is as likely as not that the NEC ceiling will be
met.
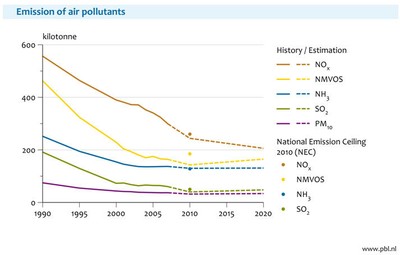
Figure 7: Emissions of
air pollutants within the Netherlands
have declined since 1990. Source: http://www.pbl.nl/nl/publicaties/2009/realisatie-milieudoelen/index.html
Number of streets where limit values
are exceeded will strongly decline
With current and proposed national
and EU legislation, the length of roads where exceedances of limit values for
PM10 and NO2 are likely (shown in red) or as likely as not (shown in
yellow) will continue to decline (Figure 8). In the Netherlands, also local measures
are being developed whose effects are not accounted for in Figure 8.
Exceedances will be more persistent along roads in the inner cities than along
motorways, because of the higher urban background concentrations in urban
cities and worse dispersion characteristics.
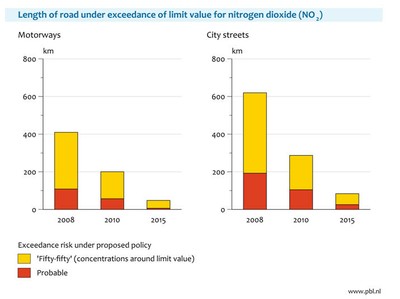
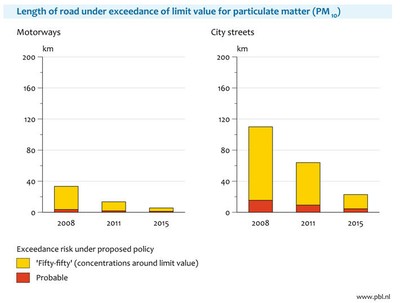
Figure 8: Exceedances of
air quality limit values along motorways and city streets for NO2
(top) and PM10 (bottom). These exceedances are to be resolved through measures
by local authorities. Source: http://www.pbl.nl/nl/publicaties/2009/Concentratiekaarten-voor-grootschalige-luchtverontreiniging-in-Nederland.-Rapportage-2009.html
Premature mortality by particulate
matter is projected to decline further
If proposed national and EU policies
are put in place, so that the objectives of the thematic strategy on air pollution
are met, the number of life-years lost will continue to decline up to 2020 (Figure
9). In Figure 9, it is assumed that health effects are caused by total PM2.5,
irrespective of chemical composition.
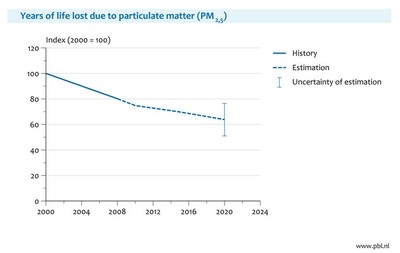
Figure 9: Years of life lost, assuming
that all PM2.5 is equally health relevant, irrespective of chemical
composition. Source: http://www.pbl.nl/nl/publicaties/2009/milieubalans/index.html
Critical loads
continue to be exceeded by 2020
About 60 % of the Dutch nature is
exposed to nitrogen deposition above critical loads, leading to loss of
biodiversity. Although emissions will decline, excess nitrogen deposition will
remain to pose a major pressure to many natural habitats in the next decade(s).
More information is available at: http://www.pbl.nl/nl/publicaties/2009/natuurbalans/index.html
Document Actions
Share with others